RADIUS gateways
The PingOne Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) Gateway is a lightweight RADIUS server that acts as a bridge between an on-premise VPN or remote access system and PingOne.
You can use a RADIUS gateway to orchestrate user authentication flows by leveraging the PingOne DaVinci orchestration engine. After you have configured a RADIUS gateway, users must follow a series of steps, as defined in your DaVinci flow, to gain access to your VPN. You can customize the DaVinci flow to include steps, such as user credential validation and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
The RADIUS gateway currently supports the PAP, MS-CHAP v2, and EAP-MSCHAPv2 protocols. You can also incorporate your Network Protocol Server (NPS) into a flow, if required. If an NPS is incorporated into the flow, after authenticating successfully, the NPS attributes are extracted from the authentication response and sent to the RADIUS client.
The following diagrams provide examples of a general RADIUS gateway authentication flow for each protocol using PingID mobile app to authenticate. The actual configuration varies depending on your organizational infrastructure considerations and policies.
Example of a RADIUS gateway flow using the PAP protocol without NPS
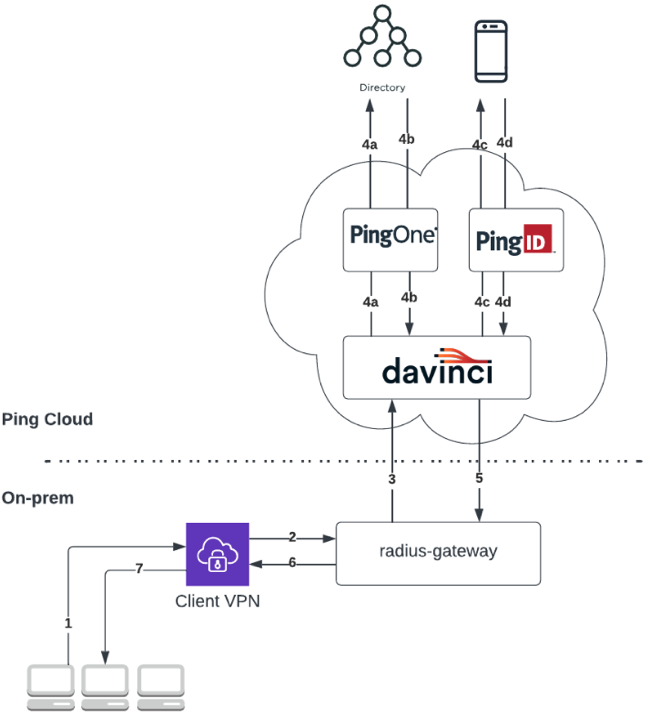
-
A user opens a VPN sign-on window and enters their username and password.
-
The VPN client sends their details to the RADIUS server running in the RADIUS gateway.
-
The RADIUS gateway initiates a DaVinci flow policy.
-
The DaVinci flow executes the following steps:
-
DaVinci invokes the PingOne connector step to initiate credential validation.
-
The user credentials are validated against a directory (in this example, PingOne Directory).
-
DaVinci invokes the PingID connector step and the PingID server initiates a second-factor authentication. The user receives a push notification to the relevant device.
-
The user approves the push notification.
-
-
The DaVinci flow is finalized and a response is sent back to the RADIUS gateway.
-
The RADIUS gateway returns a response to the VPN.
-
The VPN forwards the response, granting or denying access to the user.
Example of the RADIUS gateway using NPS
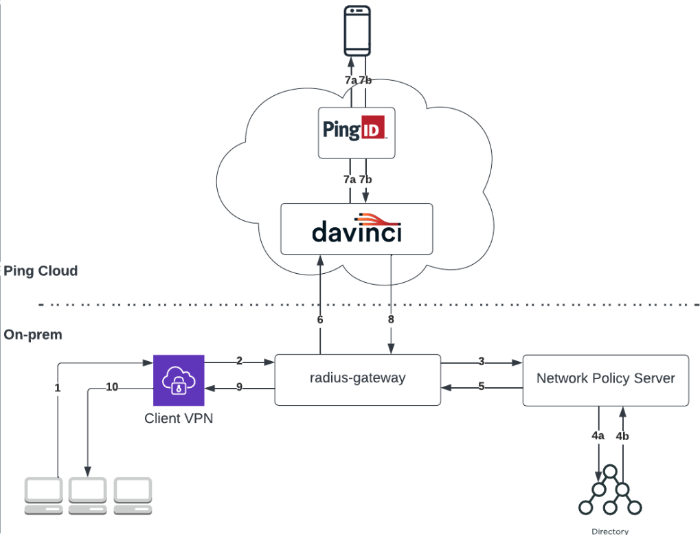
This flow can be used with advanced protocols, such as MS-CHAP v2, or PAP.
-
A user opens a VPN sign-on window and enters their username and password.
-
The VPN client sends their details to the RADIUS server running in the RADIUS gateway.
-
The RADIUS gateway forwards the details to the NPS.
-
The NPS validates the user credentials against its directory.
-
The NPS returns the response to the RADIUS gateway.
-
If the credentials are correct, the RADIUS gateway initiates a DaVinci flow policy.
-
The DaVinci flow executes the following steps:
-
DaVinci invokes the PingID connector step and the PingID server initiates a second factor authentication. The user receives a push notification to the relevant device.
-
The user approves the push notification.
-
-
The DaVinci flow is finalized and a response is sent back to the RADIUS gateway.
-
The RADIUS gateway returns a response to the VPN.
-
The VPN forwards the response, granting or denying access to the user.