RADIUS authentication
RAPID only
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a networking protocol specified in RFC 2865. It ensures that users or devices attempting to connect to a network are properly authenticated, safeguarding access and preventing unauthorized use.
It operates using a client/server model, where devices such as VPN concentrators, routers, and Wi-Fi access points are the RADIUS clients. Using the RADIUS protocol, they converse with RADIUS servers to authenticate users or devices attempting to access the network.
The conversation between RADIUS clients and servers happens through the exchange of packets. There are four types of packets used in the authentication process:
Access-Request-
The client sends an
Access-Requestpacket to the server to start a new authentication conversation, or to respond to a previous response in an existing conversation and provide requested information.This packet always contains the username and password but can contain additional information.
For example, the presence of the optional
Statefield indicates that a packet is part of an existing authentication conversation. This field doesn’t exist when it’s a new conversation. Access-Accept-
The server sends an
Access-Acceptpacket to the client to indicate a successful authentication. Access-Reject-
The server sends an
Access-Rejectpacket to the client to indicate a failed authentication. Access-Challenge-
The server sends an
Access-Challengepacket to the client to request more information from the user or device that’s authenticating.This packet is sent only if the RADIUS server requires additional information beyond the username and password, such as a one-time password (OTP) for multi-factor authentication (MFA).
When this packet is sent, it’s followed by another
Access-Requestpacket from the client that contains the requested information and theStatefield to associate the request with the existing conversation.
Advanced Identity Cloud as a RADIUS client
The following diagram illustrates the flow of packets between Advanced Identity Cloud (the RADIUS client) and the RADIUS server during an authentication conversation, where the RADIUS server requests a OTP from the user:
All conversations between Advanced Identity Cloud and the RADIUS server are secured with a shared secret (am.authentication.nodes.radius.identifier.secret).
Configure RADIUS authentication
Advanced Identity Cloud provides two authentication nodes to handle RADIUS authentication, where Advanced Identity Cloud is acting as a RADIUS client:
- RADIUS Decision node
-
The RADIUS Decision node performs authentication with the RADIUS server.
The node performs the following actions:
-
Sends an
Access-Requestpacket to the RADIUS server to initiate the authentication request. -
Handles the RADIUS server’s response to determine the outcome of the authentication attempt.
-
Sends additional
Access-Requestpackets if the RADIUS server responds with anAccess-Challengepacket requesting more information from the user.
-
- RADIUS Challenge Collector node
-
The RADIUS Challenge Collector node presents challenge messages to users, such as requesting an OTP, and collects their response.
Create an authentication journey using these nodes to implement RADIUS authentication:
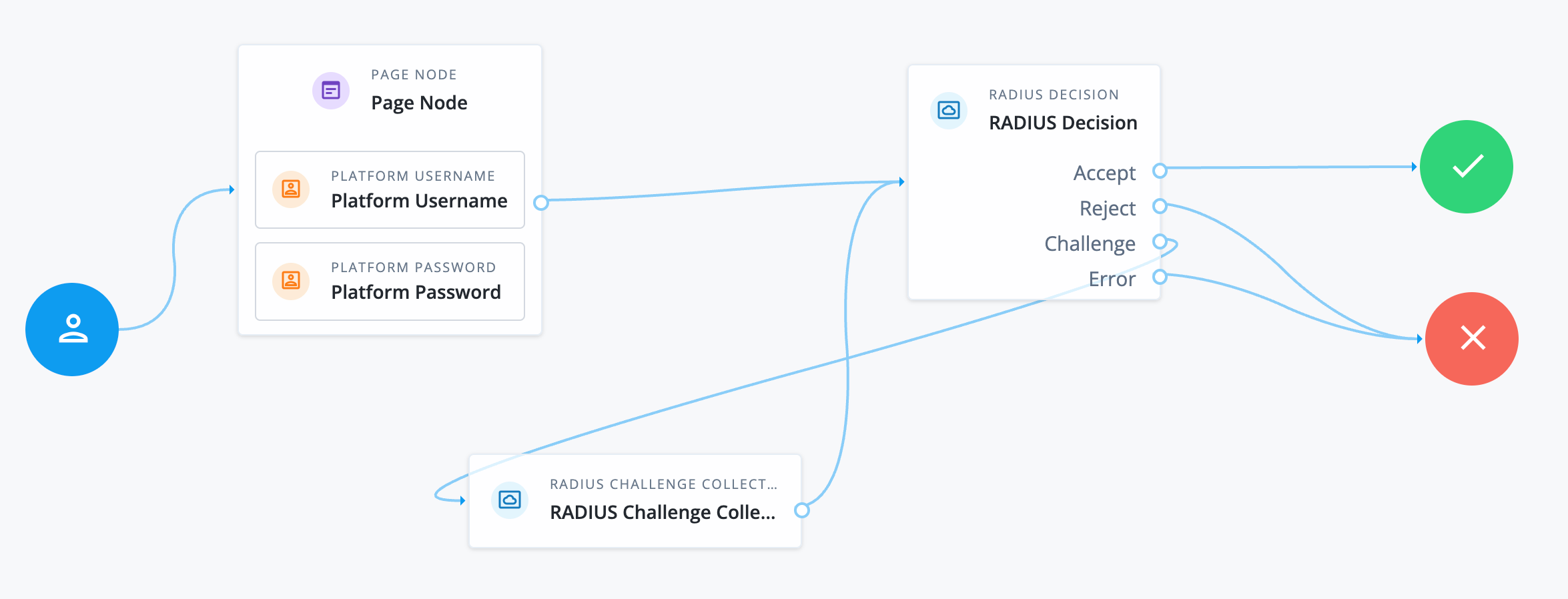
Learn more in the RADIUS authentication example.