Configure journeys
This table outlines the high-level tasks for configuring authentication journeys:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
Specify the identity object a journey should use. For example |
|
Disable journeys during development or when they aren’t in use to enhance security. |
|
Prevent an inner journey from being called directly, ensuring it’s only used within its parent journey. |
|
Force a journey to execute on every authentication attempt, even if a valid session already exists. |
|
Create a journey that completes successfully without creating an authenticated session, ideal for tasks like delegated administration. |
|
Indicate a journey can only be used for transactional authentication purposes, including backchannel authentication, OAuth 2.0 app journeys, SAML 2.0 app journeys, and transactional authorization. |
|
Override the maximum duration of the journey session for a specific journey, for example, to allow more time for an email verification step. |
|
Set custom session idle and maximum timeout values for authenticated sessions created by a specific journey. |
Specify the identity object type for a journey
Journeys assume a specific identity object type. The nodes in the journey use this object type to
verify the identity, for example, users, roles, or organizations. Only objects of type user can authenticate.
The default journeys provided with Advanced Identity Cloud assume the object authenticating through the journey is a realm-name user, for example Alpha realm - Users or Bravo realm - Users.
When you create a new journey, you select the object type in the Identity Object list.
To change the object type of an existing journey:
-
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console select Journeys > Journey name > Edit.
-
On the journey page, click the ellipses () at the top right of the page, then click Edit details.
-
Select a new object type in the Identity Object list.
Enable and disable an authentication journey
Custom authentication journeys are enabled by default, when they are saved. For security purposes, you can disable custom authentication journeys during development and testing, to prevent accidentally allowing access through these journeys. Rather than having unused authentication journeys enabled, you should disable the default authentication journeys until you need them.
When a user attempts to authenticate through a disabled journey, Advanced Identity Cloud returns a Tree does not exist error.
To enable or disable an authentication journey through the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, follow the steps to deactivate journeys.
To enable or disable an authentication journey through the REST API, send a PUT request to update the journey configuration.
Specify the journey ID, the nodes in the journey, and set the enabled flag.
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"enabled": false
}' \
'https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree'
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": false,
"enabled": false,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}Disable direct access through an inner journey
An inner (or child) journey lets you nest authentication logic. There is no limit to the depth of nesting.
You configure an inner journey like any other journey and call it from a parent journey using an Inner Tree Evaluator node.
You might want to hide inner journeys as complete services. In other words, you might want to prevent users from authenticating directly through a inner journey, either for security reasons or simply because the inner journey is insufficient as a complete authentication service. Additionally, inner journeys can’t be used as transactional authentication journeys.
To use the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console to ensure an inner journey is only called from its parent, enable Inner journey when you create a custom journey.
To configure an inner journey over REST, send a PUT request to update the journey configuration.
Specify the journey ID, the nodes in the journey, and set the innerTreeOnly property to true.
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"innerTreeOnly": true
}' \
'https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": true,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}|
To find out if the current journey is configured as an inner journey only,
include a Scripted Decision node with a script that calls Learn more in Get journey details. |
Configure an authentication journey to always run
You can set a journey to always execute whether a user has already authenticated successfully and a session exists or not. If enabled, the journey runs even when the session was created through a different journey and irrespective of the value of the ForceAuth parameter.
If you have configured an app journey, for example, by associating a journey with a SAML 2.0 application, then you don’t need to configure the journey to always run because this is default functionality for app journeys.
|
You can’t configure a journey to always run when it’s set as the default journey. Because the default journey is often used as a fallback option for many authentication flows, for example, for Ping SDKs flows over REST, a forced execution of a journey could inadvertently lead to unexpected behavior. Also, to prevent unexpected behavior in the authentication flow, don’t configure a journey to always run when it’s mapped to the default ACR. |
If a user successfully logs in using a specific authentication journey and then tries to reauthenticate to the same journey while the session is still valid, the default behavior is for the authentication flow to skip the processing of the journey.
For example, the Set Session Properties node is never run in this scenario:
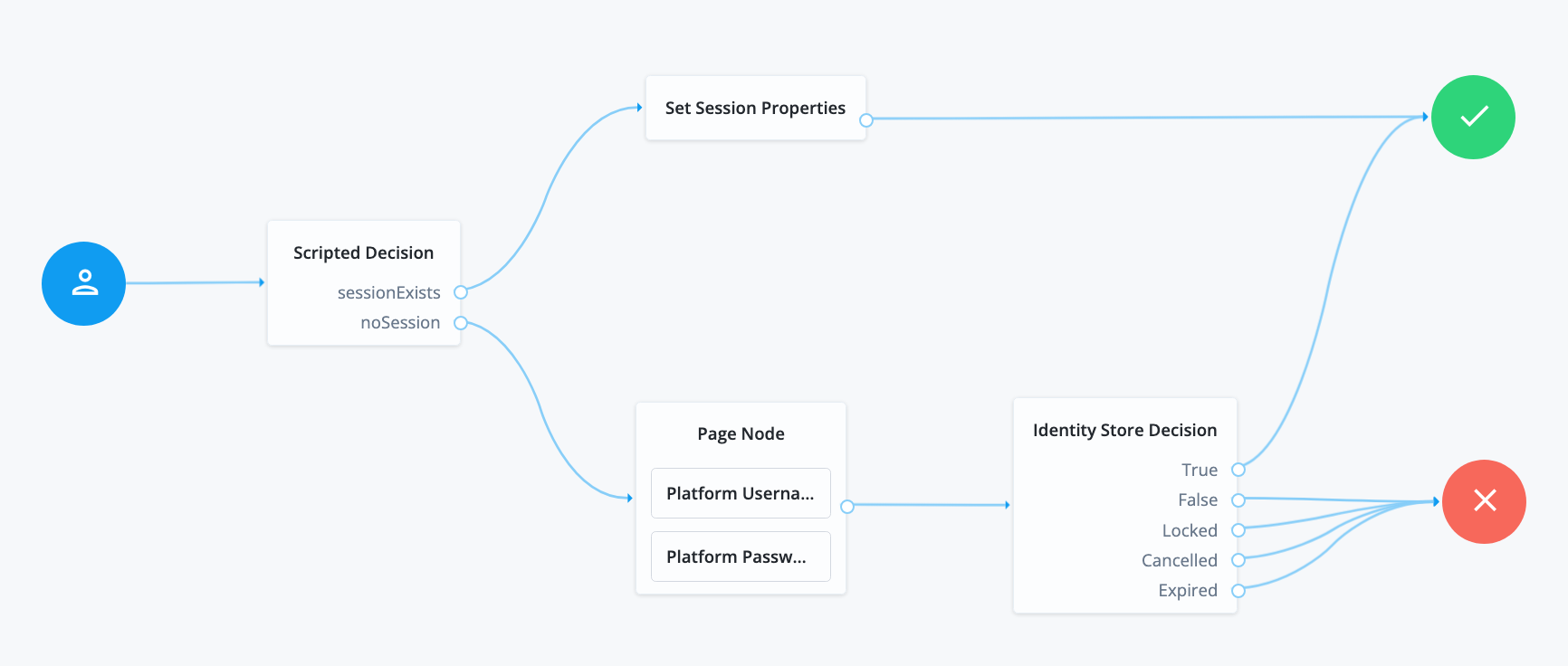
To use the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console to ensure the journey always runs and sets the session property even when a valid user session exists, enable Run journey for all users regardless of current session when you create a custom journey.
Learn more in Always run journeys.
Alternatively, set the mustRun property to true in the journey configuration by sending a PUT request to the /trees endpoint.
Include the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey.
To make sure the journey always runs and sets the session property even when a
valid authenticated session exists, set the mustRun property to true in the journey configuration by sending a PUT
request to
the /trees endpoint.
Include the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey:
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "83fa0ce2-1b0f-4f8f-83fb-0d2648339797",
"nodes": {
...
},
"mustRun": true
}' \
'https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": true,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}Configure a no session journey
A no session journey doesn’t result in an authenticated session when it successfully completes.
A common use case for a no session journey is a delegated admin task, such as an administrator changing a user’s password. In this scenario, you don’t want an authenticated session to be created when the administrator enters the credentials of the user whose password they are changing.
|
This can also be achieved by setting the If the |
To configure a no session journey, set the noSession property to true in the journey configuration.
Send a PUT request to update the journey configuration, including the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey.
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"noSession": true
}' \
"https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"noSession": true,
"mustRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}Configure a transactional authentication journey
In Advanced Identity Cloud, certain advanced authentication flows initiate a temporary, secure process known as a transaction to handle a specific authentication or authorization event.
You can configure journeys for these flows as transactional authentication journeys to manage the user interaction required to complete the transaction. This prevents users from authenticating directly through the journey, either for security reasons or because the transactional journey is insufficient as a complete authentication service. Additionally, transactional authentication journeys can’t be used as child journeys.
|
You don’t have to configure the journey used in a transactional flow as a transactional authentication journey. |
A transactional authentication journey only runs when Advanced Identity Cloud starts a transaction, which happens when Advanced Identity Cloud does one of the following:
-
Initializes backchannel authentication using either the
/authenticate/backchannel/initializeendpoint or the Backchannel Initialize node. -
Runs a SAML 2.0 app journey for a remote SP.
-
Runs an OAuth 2.0 app journey when Advanced Identity Cloud is acting as an authorization server.
-
Enforces a transactional authorization policy.
To configure a transactional authentication journey, set the transactionalOnly property to true in the journey configuration.
Send a PUT request to update the journey configuration, including the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey.
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"transactionalOnly": true
}' \
"https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "1081620278",
"uiConfig": {},
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": true,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}Configure journey session duration in a journey
The maximum duration of a journey session is derived by Advanced Identity Cloud as described in Maximum duration.
You can override realm level duration values in an individual journey if required. For example, a journey that requires email verification could have a longer duration than a simple journey that authenticates users with a username and password.
|
Duration values set in a journey can be overridden at the node level. Learn more in Maximum duration. Additionally, duration values set on inner journeys are ignored. |
Learn more in Suspend journey progress.
To change the authentication journey duration, set the treeTimeout property to the required number of minutes in the journey configuration.
Send a PUT request to update the journey configuration, including the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey.
Example
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"treeTimeout": 10
}' \
"https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": false,
"treeTimeout": 10,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}Configure authenticated session timeouts in a journey
Timeout settings for an authenticated session are derived by Advanced Identity Cloud as described in Configure authenticated session timeout settings.
You can override realm level timeout values in an individual journey if required. For example, a journey that implements MFA could have a longer authenticated session timeout than a simple journey that authenticates users with a username and password.
|
Session timeouts set in a journey can be overridden at the node or user level. Learn more in Configure authenticated session timeout settings. Session timeout values set on child journeys are ignored. However, if session timeouts are set at the node level in a child journey, the updated timeouts are used in the parent journey. |
Learn more in Session termination.
To change the session timeouts in a tree, set the maximumSessionTime and maximumIdleTime properties to the
required number of minutes in the journey configuration by sending a PUT request to the /trees endpoint.
Include the journey ID and all the nodes in the journey.
Example
The following example sets the maximumSessionTime to an hour and the maximumIdleTime to 15 minutes for
authenticated sessions established through this journey:
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=2.1,resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"nodes": {
...
},
"maximumSessionTime": 60,
"maximumIdleTime": 15
}' \
"https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/json/realms/root/realms/alpha/realm-config/authentication/authenticationtrees/trees/myAuthTree"
{
"_id": "myAuthTree",
"_rev": "2070284866",
"entryNodeId": "c11e9cf8-ef48-4740-876f-6300e2f46aef",
"innerTreeOnly": false,
"maximumSessionTime": 60,
"maximumIdleTime": 15,
"noSession": false,
"mustRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"transactionalOnly": false,
"uiConfig": {},
"nodes": {
...
}
}|
To find out if the current journey is configured to always run,
include a Scripted Decision node with a script that calls Learn more in Get journey details. |