Policies in the UI
You manage authorization policies through the AM admin console native console. You can only create a policy as part of a policy set.
To configure a policy, go to Native Consoles > Access Management > Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Policy Sets and select the name of the policy set in which to configure the policy.
| To... | Action |
|---|---|
Create a policy |
Click Add a Policy. When creating a policy, specify a name, a resource type, and at least one resource. Click Create. |
Modify a policy |
Click the policy name or the pencil icon (). |
Delete a policy |
Click the delete icon () or click the policy name then x Delete. |
Policy type names
Don’t use any of the following characters in policy, policy set, or resource type names:
-
Double quotes (
") -
Plus sign (
+) -
Comma (
,) -
Less than (
<) -
Equals (
=) -
Greater than (
>) -
Backslash (
\) -
Forward slash (
/) -
Semicolon (
;) -
Null (
\u0000)
Resources
To define resources that the policy applies to:
-
Click the Resources pencil icon () or the Resources tab.
-
Select a resource type from the Resource Type list.
The resource type determines which resource patterns are available. The
OAuth2 Scoperesource type contains the same resource patterns as theURLresource type, as well as the*pattern.Use the resource patterns that are most relevant for the scopes in your environment.
Learn more about resource types in Resource types.
-
Select a resource pattern from the Resources drop-down list.
-
Replace the asterisks with values for matching resources, and click Add.
Learn more about resource patterns in Resource type patterns.
-
Optionally, click Add Resource to add more resource patterns, or click () to delete a resource pattern.
-
Save your changes.
Policy actions
To define policy actions that allow or deny access to a resource:
-
Click the Actions pencil icon () or the Actions tab.
-
Click Add an Action to select an action from the drop-down list.
-
Select whether to allow or deny the action on the resources.
-
Optionally, add further actions, or click () to delete actions.
-
Save your changes.
Conditions
To define subject and environment conditions:
-
Combine logical operators with blocks of configured parameters to create a rule set. The policy uses this rule set to filter requests for resources.
-
Use drag and drop to nest logical operators at multiple levels to create complex rule sets.
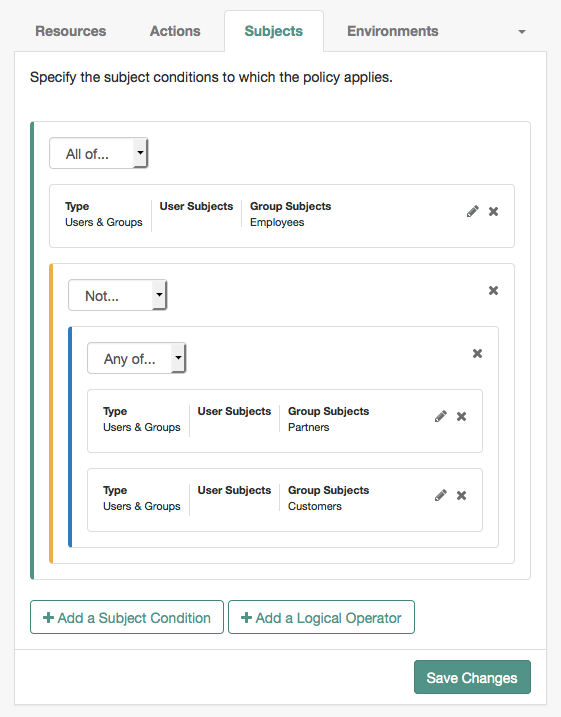
-
A gray horizontal bar indicates a valid point to drop a block.

Subjects
To define the subject conditions that the policy applies to:
-
Click Add a Subject Condition, choose the type from the drop-down menu, and provide any required subject values.
-
When complete, click the check icon () and drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set.
-
To add a logical operator, click Add a Logical Operator, choose between
All Of,Not, andAny Offrom the drop-down list, and drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set. -
To edit a condition, click the edit icon (), or click () to delete.
-
Continue combining logical operators and subject conditions and click Save Changes when you’ve finished.
| Subject condition types | Description |
|---|---|
Authenticated Users |
Any user that has successfully authenticated with Advanced Identity Cloud. |
Users & Groups |
Search for and select one or more users or groups under the Realms > Realm Name > Identities or the Groups tab. |
OpenID Connect/Jwt Claim |
Validate a claim within a JSON Web Token (JWT). Type the name of the claim to validate in the Claim Name field, for example, Repeat the step to enter additional claims. The claim(s) will be part of the JWT payload together with the JWT header and signature. The JWT is sent in the authorization header of the bearer token. This condition type only supports string equality comparisons, and is case-sensitive. |
Never Match |
Never match any subject. This disables the policy. If you do not set a subject condition, To match regardless of the subject, configure a |
Environments
To define the environment conditions the policy applies to:
-
Click Add an Environment Condition, select an environment condition type from the Type list, and provide any required values.
The fields differ, according to the type you’ve selected. Learn more in Environment condition types.
Scriptis the only environment condition available for OAuth 2.0 policies. -
When complete, click the check icon () button and drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set.
-
To add a logical operator, click Add a Logical Operator, choose between
All Of,Not, andAny Offrom the drop-down list, and drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set. -
To edit a condition, click the edit icon (), or click () to delete.
-
Continue combining logical operators and subject conditions and click Save Changes when you’ve finished.
| Environment condition type | Description | Additional fields | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Active Session Time |
Set a condition for the maximum duration the authenticated session has been active. |
|
||
Authentication Level (greater than or equal to) |
The policy tests the required authentication level. |
|
||
Authentication Level (less than or equal to) |
The policy tests the required authentication level. |
|
||
Authentication by Module Instance |
This property doesn’t apply to Advanced Identity Cloud. |
|||
Authentication by Service |
The policy tests the authentication journey used. |
|
||
Authentication to a Realm |
The policy evaluates the realm to which the end user authenticated. A session can belong to only one realm. Session upgrade between realms is not allowed. |
|
||
Current Session Properties |
The policy evaluates property values set in the authenticated session. |
|
||
IDM User |
Lets you query an IDM resource to form the basis of the policy evaluation. |
|
||
IPv4 Address/DNS Name |
The policy evaluates the IP version 4 address from which the request originated. The IP address is taken from the |
|
||
IPv6 Address/DNS Name |
The policy evaluates the IP version 6 address from which the request originated. The IP address is taken from the |
|
||
Identity Membership |
The policy evaluates the user’s UUID. |
For example, use this type to filter requests on the identity of a Web Service Client (WSC).
|
||
OAuth2 Scope |
The policy evaluates whether an authorization request includes all the specified OAuth 2.0 scopes. |
Separate multiple scope strings with spaces, for example, Scope strings match regardless of the order in which they occur, so The condition is also met when additional scope strings are provided beyond those required to match the specified list.
For example, if the condition specifies |
||
Resource/Environment/IP Address |
The policy evaluates a complex condition, such as whether the end user is making a request from a specific host, and has also authenticated in a particular way. |
The If the The available parameters for the
The IP address can be IPv4, IPv6, or a hybrid of the two.
Example: |
||
Script |
The policy evaluates the outcome of a JavaScript. |
|
||
Time (day, date, time, and timezone) |
The policy evaluates a time condition. |
Set values in start:end pairs.
Example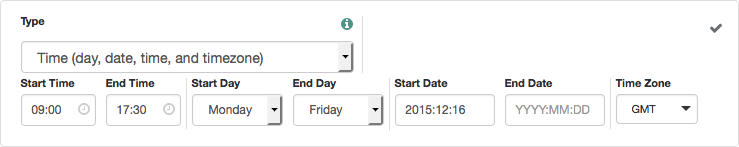
|
||
Transaction |
The policy evaluates successful completion of a transactional authorization. Transactional authorization requires the end user to authenticate for each access to the resource. |
|
||
| The LDAP Filter Condition isn’t supported in Advanced Identity Cloud. |
Response attributes
Add user attributes from the identity repository as response attributes—either as subject attribute or static attributes—to the request header at policy decision time.
Note that response attributes are not available for the OAuth2 Scope resource type.
The web or Java agent for the protected resources/applications, or the protected resources/applications themselves, retrieve the policy response attributes to customize the application.
To define response attributes in the policy:
-
Click the Response Attributes edit icon () or the Response Attributes tab.
-
To add subject attributes, select them from the Subject attributes drop-down list.
To remove an entry, select the value, and click Delete (Windows/GNU/Linux) or Backspace (Mac OS X).
-
To add a static attribute, specify the key-value pair for each static attribute. Enter the Property Name and its corresponding Property Value in the fields, and click Add (+).
To edit a static attribute, click the edit icon (), or click () to delete.
-
Continue adding subject and static attributes, and when finished, click Save Changes.
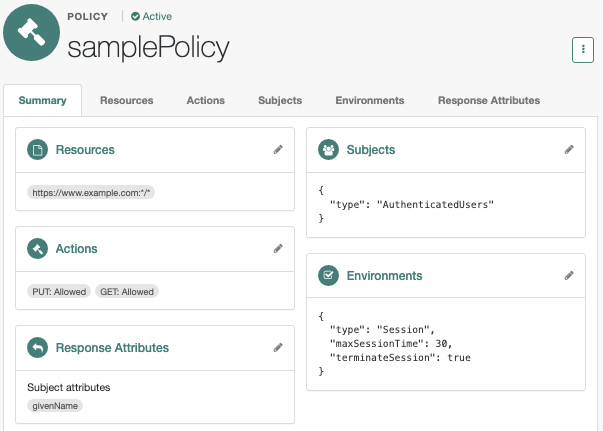
Example
This example policy requires authenticated end users to have a session no longer than 30 minutes
to access resources at https://www.example.com:*/*.
|
Before testing your OAuth 2.0 policies, ensure your OAuth 2.0 provider is configured to interact with Advanced Identity Cloud’s authorization service:
For more information about testing OAuth 2.0 policies, refer to Dynamic OAuth 2.0 authorization. |