Outbound email service
The outbound email service sends email from IDM using a script or the REST API.
You can edit the email service over REST at the config/external.email endpoint, or in the external.email.json file in your project’s conf directory.
| IDM supports UTF-8 (non-ASCII/international) characters in email addresses, such as zoë@example.com. When sending emails to these type of addresses, the configured SMTP server must also support UTF-8. |
Email service configuration types
The outbound email service supports two email service configuration types:
-
SMTP - Email service that uses the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. Can be configured using the UI or API.
-
MS Graph API - Email service that uses the MS Graph API
sendMailendpoint. Can only be configured using the API.
International email addresses
To use international email addresses, you must:
-
Use SMTP as the provider type.
-
The SMTP provider must support international email addresses.
-
Configure
mail.mime.allowutf8=true, which is only available using the REST API or the filesystem. For more information, refer tosmtpPropertiessub-properties.
MS Graph API requirements
Use of the MS Graph API email client requires a properly configured Microsoft Azure tenant. The basic steps for configuring an Azure tenant should be used as an outline, as the specific options, menus, and features may have changed.
Configure Azure for MS Graph API mail client
-
Navigate to Azure Active Directory | App registrations.
-
Create the IDM client application:
-
From the menu bar, click + New Registration.
-
On the Register an application page, enter the application Name, such as
idm-email-client. -
For Supported account types, select the applicable option for your organization.
-
Click Register.
-
On the idm-email-client page, in the main Essentials area, record the Application (client) ID.
This is the value for clientIdin theauthsettings of the email configuration. Refer tooauth2properties.
-
-
Add a client secret:
-
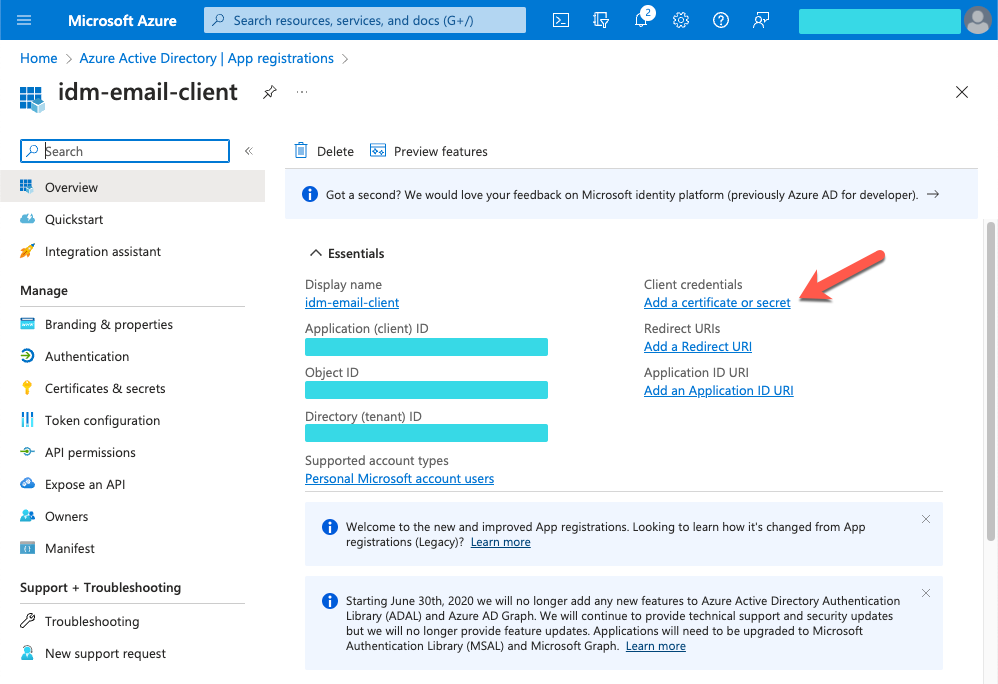
On the idm-email-client page, in the main Essentials area, click Add a certificate or secret.
Show Me
-
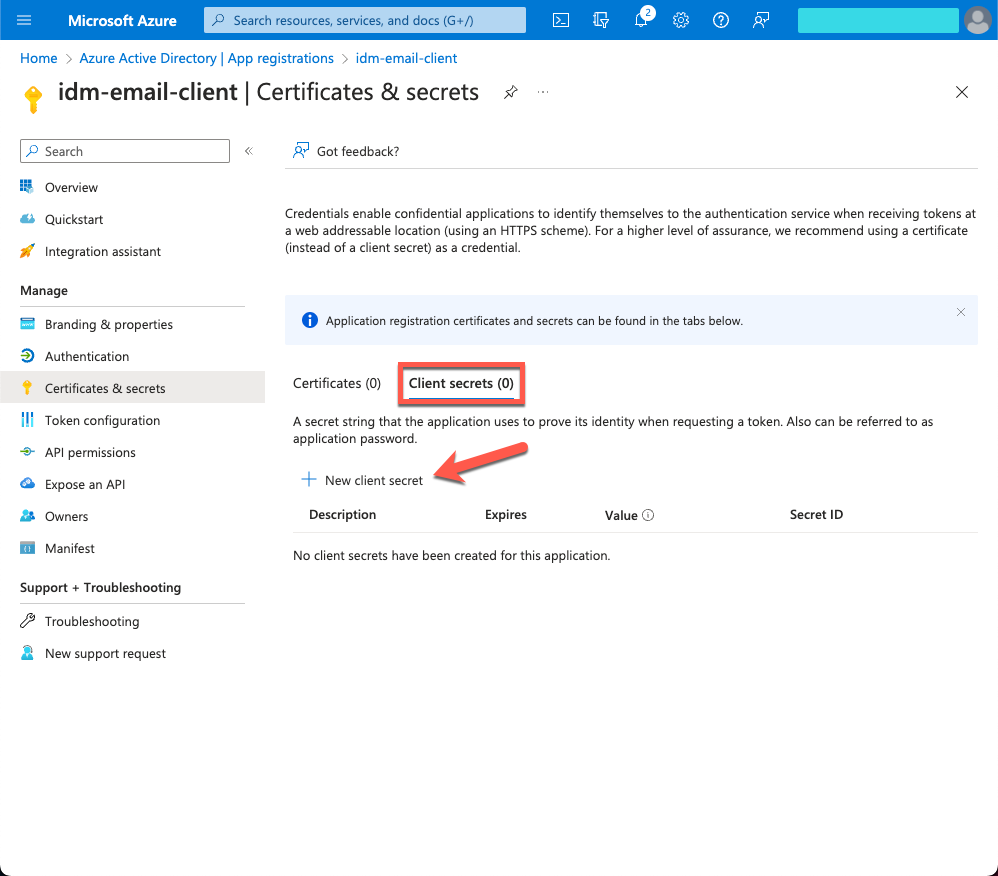
On the Certificates & secrets page, select the Client secrets tab, and click + New client secret.
Show Me
-
In the Add a client secret window, enter the details, and click Add.
-
Copy the Value and Secret ID to a secure place before leaving the Certificates & secrets page.
Use the secret Value for clientSecretin theauthsettings of the email configuration. Refer tooauth2properties.
-
-
Add API permissions:
-
From the side menu, click API permissions.
-
On the API permissions page, click + Add a permission.
-
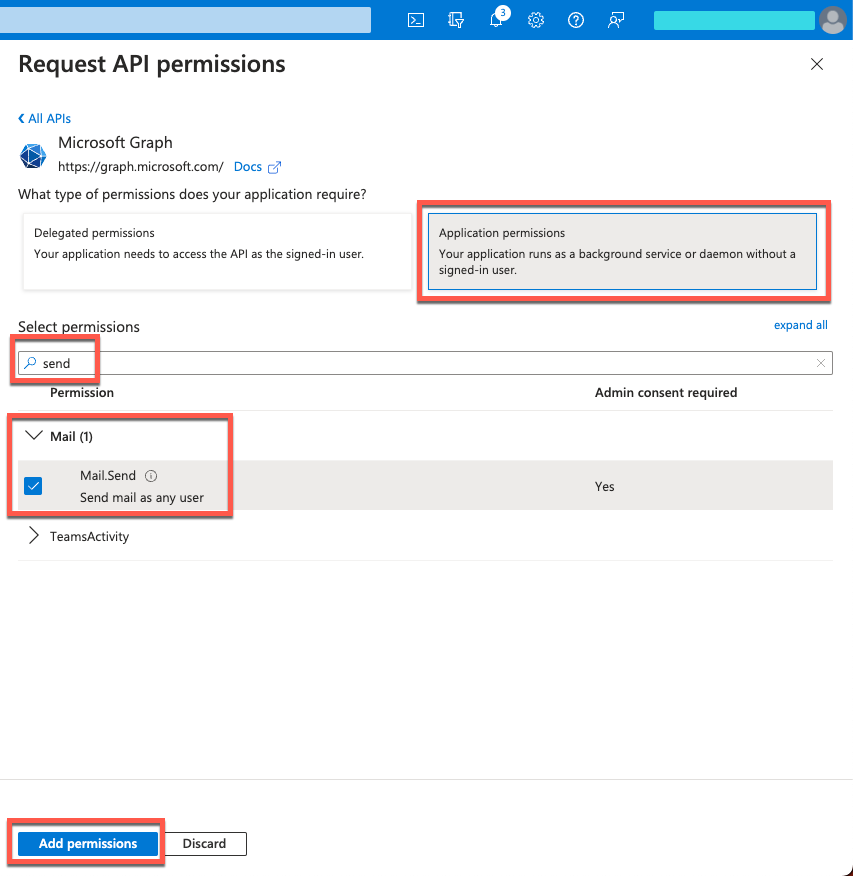
In the Request API permissions windows, select the Microsft APIs tab, and click Microsoft Graph.
-
In the What type of permissions... area, click Application permissions.
-
In the Select permissions search bar, type
send. -
Expand the Mail node, and select Mail.Send.
-
Click Add permissions.
Show Me
-
Configure outbound email
To configure the outbound email service using the admin UI, click Configure > Email Settings.
-
Edit the email configuration with the mail server details and account.
-
For the complete list of configuration options, refer to External email configuration properties.
-
For sample email configurations, refer to Sample email configuration.
-
-
Submit the configuration over REST or copy the file to your project’s
conf/directory. For example:-
REST
-
Filesystem
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "host" : "smtp.gmail.com", "port" : 587, "debug" : false, "auth" : { "enable" : true, "username" : "admin", "password" : "Passw0rd" }, "from" : "admin@example.com", "timeout" : 300000, "writetimeout" : 300000, "connectiontimeout" : 300000, "starttls" : { "enable" : true }, "ssl" : { "enable" : false }, "smtpProperties" : [ "mail.smtp.ssl.protocols=TLSv1.2", "mail.smtps.ssl.protocols=TLSv1.2", "mail.mime.allowutf8=true" ], "threadPoolSize" : 20 }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/config/external.email"cp /path/to/external.email.json /path/to/openidm/conf/
IDM encrypts the password. -
Storing MS Azure credentials as a secret
You can enable zero-downtime rotation of your clientId and clientSecret credentials by storing those values in a file system based secret store.
To configure an existing IDM external email client with an existing MS Azure tenant to use a file system secret store:
-
Add a new secret in the Microsoft Azure portal. For more information, refer to the Microsoft identity platform documentation.
-
Create the
idm.email.msgraph.credentialsfile in your file system-based secret store. The file must contain a JSON object with your secret values, such as:{ "clientId": "myClient", "clientSecret": "mySecret" } -
Update the
authproperty inconf/external.email.jsonto read theclientIdandclientSecretfrom the secret file using a purpose. You must set ajsonPointerproperty that identifies the matching field in the secret file:{ ... "auth": { "enable": true, "type": "oauth2", "clientId": { "$purpose": { "name" : "idm.email.msgraph.credentials", "jsonPointer" : "clientId" } }, "clientSecret" : { "$purpose" : { "name" : "idm.email.msgraph.credentials", "jsonPointer" : "clientSecret" } }, "tokenEndpoint" : "https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token", "scope" : [ "https://graph.microsoft.com/.default" ], "scopeDelimiter" : " ", "grantType" : "client_credentials" } }
If you use a secret that only stores a password, you only need to update the clientSecret value in conf/external.email.json.
|
Sample email configuration
This sample email configuration sets up the outbound email service:
-
SMTP
-
MS Graph API
{
"host" : "smtp.gmail.com",
"port" : 587,
"debug" : false,
"auth" : {
"enable" : true,
"username" : "xxxxxxxx",
"password" : "xxxxxxxx"
},
"timeout" : 300000,
"writetimeout" : 300000,
"connectiontimeout" : 300000,
"starttls" : {
"enable" : true
},
"ssl" : {
"enable" : false
},
"smtpProperties" : [
"mail.smtp.ssl.protocols=TLSv1.2",
"mail.smtps.ssl.protocols=TLSv1.2"
],
"threadPoolSize" : 20
}{
"type" : "msgraph",
"mailEndpoint" : "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/users/example@myTenant.onmicrosoft.com/sendMail",
"from" : "example@myTenant.onmicrosoft.com",
"auth" : {
"enable" : true,
"type" : "oauth2",
"clientId" : "clientId",
"clientSecret" : "clientSecret",
"tokenEndpoint" : "https://login.microsoftonline.com/myTenant.onmicrosoft.com/oauth2/v2.0/token",
"scope" : [
"https://graph.microsoft.com/.default"
]
},
"timeout" : 300000,
"writetimeout" : 300000,
"connectiontimeout" : 300000,
"threadPoolSize" : 20
}External email configuration properties
The msgraph type also supports the External REST configuration properties.
| Property | Description | Required? / Type Support |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The email service type, |
No |
||
|
The URI for the MS Graph API Typical format: |
Yes Only for |
||
|
The host name or IP address of the SMTP server. This can be the |
Yes Only for |
||
|
SMTP server port number, such as 25, 465, or 587.
|
Yes Only for |
||
|
When set to |
No Only for |
||
|
Specifies a default From: address which displays when users receive emails from IDM.
|
No |
||
|
Contains authentication detail sub-properties. Refer to the authentication sub-properties table for all options. |
Yes Required sub-properties vary based on |
||
|
If |
No Only for |
||
|
Set |
No Only for |
||
|
SMTP options. Refer to the SMTP sub-properties table for all options. |
No Only for |
||
|
Emails are sent in separate threads managed by a thread pool. This property sets the number of concurrent emails that can be handled at a specific time. The default thread pool size (if none is specified) is |
No |
||
|
The socket connection timeout, in milliseconds. The default connection timeout (if none is specified) is |
No |
||
|
The socket read timeout, in milliseconds. The default read timeout (if none is specified) is |
No Only for |
||
|
The socket write timeout, in milliseconds. The default write timeout (if none is specified) is |
No Only for |
| Property | Description | Required? / Type Support |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Whether you need login credentials to connect to the server/API.
|
Yes |
||
|
Account used to connect to the server/API. |
No |
||
|
Password used to connect to the server/API. |
No |
||
|
Authentication type used to connect to the server/API:
|
Yes |
||
The following properties are only applicable when the |
||||
|
clientId used to request an access token from the token endpoint. Obtained during Azure application creation. To store as a secret, refer to Storing MS Azure credentials as a secret. |
Yes |
||
|
clientSecret used to request an access token from the token endpoint. Obtained during Azure application creation. To store as a secret, refer to Storing MS Azure credentials as a secret. |
Yes |
||
|
OAuth2 token endpoint. Typical format: |
Yes |
||
|
Requested OAuth2 scopes in a JSON array of strings. |
Yes |
||
|
Scope delimiter to use. Defaults to space. |
No |
||
|
The only supported grant type is |
No |
||
| Property | Description | Required? / Type Support |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The enabled SMTP SSL connection protocols. Protocols are specified as a whitespace-separated list. The default protocol is TLSv1.2. |
No Only for |
||
|
The enabled SMTPS SSL connection protocols. Protocols are specified as a whitespace-separated list. The default protocol is TLSv1.2. |
No Only for |
||
|
Adds support for UTF8 (Non-ASCII) characters in the local part of email addresses (everything before the
|
No Only for |
Email rate limiting
No rate limiting is applied to password reset emails, or any emails sent by the IDM server. This means that an attacker can potentially spam a known user account with an infinite number of emails, filling that user’s inbox. In the case of password reset, the spam attack can obscure an actual password reset attempt.
In a production environment, you must configure email rate limiting through the network infrastructure in which IDM runs. Configure the network infrastructure to detect and prevent frequent repeated requests to publicly accessible web pages, such as the password reset page. You can also handle rate limiting within your email server.