Client application registration
OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect client applications must register with AM before they can connect.
Registration involves setting up a client application profile in one of the following ways:
-
Using the AM admin UI to Create a client profile.
-
Programmatically with Dynamic client registration.
-
Calling the AM REST endpoint.
Create a client profile
-
In the AM admin UI, go to Realms > Realm Name > Applications > OAuth 2.0 > Clients.
-
Click Add Client and provide values for Client ID, Client secret, Redirection URIs, Scope(s), and Default Scope(s).
-
Click Create to create the profile.
-
Adjust the configuration as needed, using the inline help and the following documentation:
Core
- Group
-
Set this field if you have configured an OAuth 2.0 client group.
- Status
-
Whether this client is Active (can be used) or Inactive.
- Client secret
-
The client secret, as described in RFC 6749 (Client Password). If you don’t store the secret in a secret store, the client uses this Client secret to authenticate to PingAM. This property is ignored if you specify a Secret Label Identifier and the corresponding secret mapping.
- Secret Label Identifier
-
PingAM uses this identifier to create specific secret labels for this OAuth 2.0 client using the following templates:
-
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.secretfor the Client secret -
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.jwt.public.keyfor the Client JWT Bearer Public Key -
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.mtls.trusted.certfor the mTLS Self-Signed Certificate -
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.id.token.enc.public.keyfor the Client ID Token Public Encryption Key
where identifier is the value of Secret Label Identifier.
-
Using the identifier
The identifier can only contain alphanumeric characters
a-z,A-Z,0-9, and periods (.). It can’t start or end with a period.If you set a Secret Label Identifier and PingAM finds a matching secret in a secret store, the corresponding configuration property (for example, Client secret) is ignored.
As a best practice, use a different Secret Label Identifier per OAuth 2.0 client, and rotate secrets periodically. For OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect 1.0 clients, PingAM uses the active secret as the client shared secret key when signing the contents of the
requestparameter with HMAC-based algorithms, such as HS256. If you don’t set a Secret Label Identifier, PingAM uses the Client secret as the shared secret key.If you have enabled Scalable OAuth 2.0 clients, you can’t use the Secret Label Identifier setting when there are more than 1000 clients in a realm.
- Client type
-
The client type.
Confidential clients maintain the confidentiality of their credentials; for example, a web application running on a server where its credentials are protected. Public clients run the risk of exposing their passwords to a host or user agent; for example, a JavaScript client running in a browser.
- Allow wildcard ports in redirection URIs
-
Whether AM allows the use of wildcards (* characters) in the redirection URI port to match one or more ports.
The URL configured in the redirection URI must be either
localhost,127.0.01, or::1. For example,http://localhost:*/,https://127.0.0.1:80*/, orhttps://[::1]:*443/.For example, enable this setting for desktop apps that start a web server on a random free port during the OAuth 2.0 flow.
- Redirection URIs
-
The client redirection endpoint URIs as described in RFC 6749 (Redirection Endpoint). AM’s OAuth 2.0 authorization service redirects the resource owner’s user agent to this endpoint during the authorization code grant process. If your client has more than one redirection URI, you must specify the redirection URI to use in the authorization request.
Redirection URI values must NOT contain a fragment () and must be an exact match. Wildcards are only considered special characters for ports when you enable [.label]#Allow wildcard ports in redirection URIs.
OpenID Connect clients require redirection URIs.
- Scope(s)
-
The scopes to present to the resource owner when the resource owner must authorize client access to protected resources.
The
openidscope is required for OpenID Connect clients. This scope indicates that the client is making an OpenID Connect request to the authorization server.Enter scopes as simple strings; for example,
openid,read,email,profile, or as a pipe-separated string in the format:scope|locale|localized description. For example,read|en|Permission to view email messages.Locale strings have the format:
language_country_variant. For example,en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If you omit thelocaleand pipe, AM displays the localized description to users with undefined locales. If you omit the localized description, nothing is displayed to all users. For example, a scope ofread|lets the client use thereadscope but doesn’t display it to the user when requested.AM reserves special scopes to let resource servers introspect tokens issued to other clients. Learn more in Special Scopes.
Learn more about scopes, default scopes, and how AM uses them in OAuth 2.0 scopes.
- Default Scope(s)
-
Scopes AM uses when the client doesn’t request any scopes during a grant flow, in
scopeorscope|locale|localized descriptionformat.+ Scopes defined in this property take the same format as those defined in Scope(s).
+ Learn more about scopes, default scopes, and how AM uses them in OAuth 2.0 scopes.
- Client Name
-
A human-readable name for the client.
- Authorization Code Lifetime (seconds)
-
The time, in seconds, that an authorization code is valid. If you set this property to zero, PingAM uses the authorization code lifetime of the OAuth2 provider.
Default:
0 - Refresh Token Lifetime (seconds)
-
The time, in seconds, that a refresh token is valid. If you set this property to zero, PingAM uses the refresh token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider. If you set this property to
-1, the token never expires.Default:
0 - Access Token Lifetime (seconds)
-
The time, in seconds, that an access token is valid. If you set this property to zero, PingAM uses the access token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider.
Default:
0
Advanced
- Token Exchange Auth Level
-
The authentication level that AM sets for tokens created through Token exchange if the subject token doesn’t have an initial authentication level; for example, when exchanging an ID token for an access token.
Default: 0
- Display name
-
The client name to display to the resource owner when the resource owner is asked to authorize client access to protected resources. Valid formats include
nameorlocale|localized name.The Display name can be entered as a single string or as a pipe-separated string for locale and localized name, for example,
en|My Example Company.Locale strings have the format:
language_country_variant. For example,en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleis omitted, the name is displayed to all users having undefined locales. - Display description
-
The client description to display to the resource owner when the resource owner is asked to authorize client access to protected resources. Valid formats include
descriptionorlocale|localized description.The Display description can be entered as a single string or as a pipe-separated string for locale and localized name, for example,
en|The company intranet is requesting the following access permission.Locale strings have the format:
language_country_variant. For example,en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleis omitted, the name is displayed to all users having undefined locales.
- JavaScript Origins
-
The origin URLs allowed by the client to make cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) requests to AM.
For example, you might add the URL of a resource server being protected by an app that uses the ForgeRock SDKs, so that it can access the OAuth 2.0 endpoints from a different domain than AM.
This property doesn’t support using a non-standard header. To use a custom header, you must create a new CORS configuration.
Wildcards aren’t supported; each value should be an exact match for the origin of the CORS request.
The global CORS service collects the value of this property from each OAuth 2.0 client, and combines it with its own configuration.
Ensure that customers allowlist all headers for CORS and OAuth 2.0 client integration with AM. Learn more in Configure CORS support.
- Request uris
-
The
request_urivalues that a dynamic client would pre-register.URIs must be pre-registered in this field before the client can request them in the
request_uriparameter. - Grant Types
-
The set of OAuth 2.0 grant flows allowed for this client. The following flows are available:
-
Authorization Code -
Back Channel Request -
Implicit -
Resource Owner Password Credentials -
Client Credentials -
Refresh Token -
UMA -
Device Code -
SAML2 -
Token Exchange
Default:
Authorization Code. When registering clients dynamically, if no grant types are specified in the registration request, then the defaultAuthorization Codegrant type is assumed, and configured in the client. Any grant types selected in a client must also be enabled in the OAuth 2.0 provider service. Refer to OAuth2 Provider. -
- Response Types
-
The response types that the client uses. The response type value specifies the flow that determine how the ID token and access token are returned to the client. Learn more in OAuth 2.0 Multiple Response Type Encoding Practices.
Configure this field only if the client uses OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect grant flows that interact with the
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint.The following response types are available:
-
code. Specifies that the client requests an authorization code during the Authorization code grant flow for OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect.This response type also applies to the Authorization Code grant with PKCE flows.
-
token. Specifies that the client requests an access token during the Implicit grant flow. -
id_token. Specifies that the client requests an ID token during the OpenID Connect Implicit grant flow. -
code token. Specifies that the client requests an access token and an authorization code during the OpenID Connect Hybrid grant flow. -
code id_token. Specifies that the client requests an authorization code and an ID token during the OpenID Connect Hybrid grant flow. -
code token id_token. Specifies that the client application requests an authorization code, an access token, and an ID token, during the OpenID Connect Hybrid grant flow. -
token id_token. Specifies that the client requests an access token and an ID token during the OpenID Connect Implicit grant flow.
-
- Contacts
-
The email addresses of users who administer the client.
- Token Endpoint Authentication Method
-
The authentication method with which a client authenticates to AM (as an authorization server) at the token endpoint. The authentication method applies to OIDC requests with scope
openid.-
client_secret_basic. Clients authenticate with AM (as an authorization server) using the HTTP Basic authentication scheme after receiving aclient_secretvalue. -
client_secret_post. Clients authenticate with AM (as an authorization server) by including the client credentials in the request body after receiving aclient_secretvalue. -
private_key_jwt. Clients sign a JSON web token (JWT) with a registered public key. -
tls_client_auth. Clients use a CA-signed certificate for mutual TLS authentication. -
self_signed_tls_client_auth. Clients use a self-signed certificate for mutual TLS authentication. -
none. Clients are public and don’t authenticate.Learn more in OAuth 2.0 client authentication, and Client Authentication in the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 incorporating errata set 1 specification.
-
- Sector Identifier URI
-
The value of this field must be a URL (including the
httpsscheme) that references a JSON file containing an array ofredirect_urivalues. AM uses the host component of this URL to compute pairwise subject identifiers.If you configure a single Post Logout Redirect URI, the Sector Identifier URI takes this value by default. If you configure several Post Logout Redirect URIs and specify a pairwise Subject Type, you must set a value for the Sector Identifier URI.
- Subject Type
-
The subject identifier type, which is a locally unique identifier that the client consumes. The subject type can be one of the following:
-
public. Provides the same
sub(subject) value to all clients. -
pairwise. Provides a different
sub(subject) value to each client to prevent correlation between clients.
If you specify a pairwisesubject type, read Sector Identifier URI. -
- Access Token
-
The
registration_access_tokenvalue that you provide when registering the client, and then subsequently when reading or updating the client profile. - Client URI
-
The URI containing further information about this client. The URI is displayed as a link in user-facing pages, such as consent pages.
The URI can be made locale-specific by specifying a pipe-separated string in the format: URI|locale. For example,
https://www.example.es:8443/aplicacion/informacion.html|es. - Logo URI
-
The URI of a logo for the client. The logo is displayed in user-facing pages, such as consent pages.
The logo can be made locale-specific by specifying a pipe-separated string in the format: URI|locale. For example,
https://www.example.es:8443/aplicacion/imagen.png|es. - Privacy Policy URI
-
The URI containing the client’s privacy policy documentation. The URI is displayed as a link in user-facing pages, such as consent pages.
The URI can be made locale-specific by specifying a pipe-separated string in the format: URI|locale. For example,
https://www.example.es:8443/aplicacion/legal.html|es. - Terms of Service URI
-
The URI that contains the client’s terms of service. The URI is displayed as a link in user-facing pages, such as consent pages.
The URI can be made locale-specific by specifying a pipe-separated string in the format: URI|locale. For example,
https://www.example.es:8443/aplicacion/terminos.html|es.
- Refresh Token Grace Period (seconds)
-
The time, in seconds, that a refresh token can be reused, for this client. This grace period lets the client recover seamlessly, if the response from an original refresh token request isn’t received, because of a network problem or other transient issue. During the grace period, the refresh token can be reused multiple times, if the network problem persists. When the grace period ends, the refresh token is revoked.
The refresh token grace period applies only to server-side tokens, in a one-to-one storage scheme.
This property can take the following values:
-
0The client inherits the refresh token grace period set in the OAuth 2.0 provider configuration. This is the default setting. -
-1There is no refresh token grace period for this client. -
Any positive integer up to the maximum—this value overrides the grace period set in the OAuth 2.0 provider configuration.
Having a long grace period poses a security risk. You should therefore keep the grace period as small as possible. By default, the grace period can’t exceed 120 seconds. You can override this default maximum by setting the org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.client.graceperiod.disabled advanced server property. Note, however, that exceeding the default maximum of 120 seconds isn’t recommended. -
- Implied Consent
-
Enable the implied consent feature. When enabled, the resource owner won’t be asked for consent during authorization flows. The OAuth2 Provider must also be configured to allow clients to skip consent.
- OAuth 2.0 Mix-Up Mitigation enabled
-
Enable OAuth 2.0 mix-up mitigation on the authorization server side.
Enable this setting only if this OAuth 2.0 client supports the OAuth 2.0 Mix-Up Mitigation draft, otherwise AM will fail to validate access token requests received from this client.
- Require Pushed Authorization Requests
-
If enabled, the client must use the PAR endpoint to initiate authorization requests.
Note that, even if this value is set to false, the authorization server may be configured to enforce PAR for all clients.
OpenID Connect
- Claim(s)
-
One or more claim name translations that will override those specified for the authentication session. Claims are values that are presented to the user to inform them what data is being made available to the client.
Claims can be in entered as simple strings, such as
name,email,profile, orsub, or as a pipe-separated string in the format:scope|locale|localized description. For example,name|en|Full name of user.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If you omit thelocaleand pipe, AM displays the localized description to users with undefined locales. If you omit the localized description, AM displays nothing to all users. For example, a claim ofname|lets the client use thenameclaim but doesn’t display it to the user when requested.If you don’t specify a value here, the value is computed from the OAuth 2.0 provider.
- Post Logout Redirect URIs
-
One or more allowable URIs to which AM can redirect the user-agent after the client logout process.
- Client Session URI
-
The relying party (client) URI to which the OpenID Connect Provider sends session changed notification messages using the HTML 5
postMessageAPI. - Default Max Age
-
The maximum time in seconds that a user can be authenticated. If the user last authenticated earlier than this value, the user must reauthenticate. The request parameter
max_ageoverrides this setting, if specified.Minimum value:
0. A value of0forces the user to reauthenticate rather than use an existing session that might have been set in their browser by another client.Default:
600 - Default Max Age Enabled
-
Enable the default max age feature.
- Default ACR values
-
Default Authentication Context Class Reference values.
Strings to request as Voluntary Claims by default in all incoming requests.
Values specified in the
acr_valuesrequest parameter or an individualacrclaim request override these default values. - OpenID Connect JWT Token Lifetime (seconds)
-
The time in seconds for a JWT to be valid. If this field is set to zero, the JWT token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider is used.
Don’t set a token lifetime greater than 86400 seconds (one day). Default:
0 - Backchannel Logout URL
-
The URL to where AM will send the logout token during backchannel logout.
This URL can use the http or the https scheme, and may contain a port, a path, or query parameters, depending on the implementation of the relying party. For example,
https://my-rp.example.com:443/logout.Learn more in Backchannel logout.
- Backchannel Logout Session Required
-
Indicate whether to add the session ID (
sid) to the logout token. The session ID identifies the relying party’s session with the provider.Learn more in Backchannel logout.
Signing and Encryption
AM returns an error if the administrator tries to save a client profile configuration containing an unsupported signing or encryption algorithm on a client.
For example, upon saving the configuration, AM will return an error if there is a typo on an algorithm, or a symmetric signing or encryption algorithm is configured on a public client: these algorithms are derived from the client’s secret, which public clients don’t have.
Clients registering dynamically must also send supported algorithms as part of their configuration, or AM will reject the registration request.
Different features support different algorithms. Refer to the documentation or the UI for more information.
- Json Web Key URI
-
The URI that contains the client’s public keys in JSON web key format.
When the client authenticates to AM using the
private_key_jwtmethod, AM checks this field to find the public key to validate the JWT. - JWKs URI content cache timeout in ms
-
The period of time, in milliseconds, that the content of the JWKs' URI is cached for before being refreshed. Caching the content avoids fetching it for every token encryption or validation.
Default:
3600000 - JWKs URI content cache miss cache time
-
The period of time, in milliseconds, that AM waits before fetching the URI’s content again when a key ID (
kid) isn’t in the JWK set already cached.For example, if a request comes in with a
kidthat isn’t in the cached JWKs, AM checks the value of JWKs' URI content cache miss cache time. If the amount of time specified in this property has already passed since the last time AM fetched the JWKs, AM fetches them again. Otherwise, the request is rejected.Use this property as a rate limit to prevent denial-of-service attacks against the URI.
Default:
60000 - Token Endpoint Authentication Signing Algorithm
-
The JWS algorithm that must be used for signing JWTs used to authenticate the client at the Token Endpoint.
JWTs that aren’t signed with the selected algorithm in token requests from the client using the
private_key_jwtauthentication method will be rejected.Default:
RS256 - Json Web Key
-
Raw JSON web key value containing the client’s public keys.
- ID Token Signing Algorithm
-
The signing algorithm that the ID token must be signed with.
- Enable ID Token Encryption
-
Enable ID token encryption using the specified ID token encryption algorithm.
- ID Token Encryption Algorithm
-
The algorithm that the ID token must be encrypted with.
Default value:
RSA1_5(RSAES-PKCS1-V1_5). - ID Token Encryption Method
-
The method that the ID token must be encrypted with.
Default value:
A128CBC-HS256.
- Authorization Response JWT Signing Algorithm
-
The algorithm to be used to sign an authorization response JWT.
If configured, it must match one of the values set in the
Authorization Response Signing Algorithms Supportedproperty of the OAuth2 provider service.
Default value:
RS256.- Authorization Response JWT Encryption Algorithm
-
The algorithm to be used to encrypt an authorization response JWT.
To disable encryption of the authorization response JWT, ensure this property isn’t set.
To enable encryption, set the property to a valid value. This must match one of the values set in the
Authorization Response Encryption Algorithms Supportedproperty of the OAuth2 provider service.
- Authorization Response JWT Encryption Method
-
The encryption method to secure an authorization response JWT.
If configured, it must match one of the values set in the
Authorization Response Encryption Methods Supportedproperty of the OAuth2 provider service.Default value:
A128CBC-HS256, whenAuthorization Response JWT Encryption Algorithmis set. - Client ID Token Public Encryption Key
-
The Base64-encoded public key for encrypting ID tokens.
For improved security and to support secret rotation, store this certificate as a secret in a secret store instead. Map the secret to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.id.token.enc.public.keydynamic secret label, where identifier is the value of the Secret Label Identifier set in this client’s configuration.If you specify a Secret Label Identifier and AM finds a corresponding secret mapping, it ignores the value of this field.
- Client JWT Bearer Public Key
-
The Base64-encoded X509 certificate in PEM format, containing the public key pair for signing the Client Bearer JWT. This certificate isn’t used during the signing process. It’s used to obtain the client’s JWT bearer public key. The client uses the private key to sign client authentication and access token request JWTs, while AM uses the public key for verification.
For improved security and to support secret rotation, store this certificate as a secret in a secret store instead. Map the secret to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.jwt.public.keydynamic secret label, where identifier is the value of the Secret Label Identifier set in this client’s configuration.If you specify a Secret Label Identifier and AM finds a corresponding secret mapping, it ignores the value of this field.
The following is an example of the certificate:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDETCCAfmgAwIBAgIEU8SXLj..... -----END CERTIFICATE-----You can generate a new key pair alias by using the Java
keytoolcommand. Follow the steps in To Create Key Aliases in an Existing Keystore.For example:
$ keytool \ -list \ -alias myAlias \ -rfc \ -storetype JCEKS \ -keystore myKeystore.jceks \ -keypass myKeypass \ -storepass myStorepass Alias name: myAlias Creation date: Oct 27, 2020 Entry type: PrivateKeyEntry Certificate chain length: 1 Certificate[1]: -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDETCCAfmgAwIBAgIEU8SXLj… -----END CERTIFICATE-----Learn more in JWT profile.
- mTLS Self-Signed Certificate
-
The base64-encoded X.509 certificate in PEM format that clients can use to authenticate to the
access_tokenendpoint during mutual TLS authentication.Only applies when clients use self-signed certificates to authenticate.
For improved security and to support certificate rotation, store the certificate as a secret in the secret store.
Map this secret to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.mtls.trusted.certsecret label, whereidentifieris the value of the Secret Label Identifier configured for the client on the Core tab.If you specify a Secret Label Identifier and AM finds a corresponding secret mapping, it ignores the value of this field.
Learn more in Mutual TLS.
- mTLS Subject DN
-
The distinguished name that must exactly match the subject field in the client certificate used for mutual TLS authentication. For example,
CN=myOauth2Client.Only applies when clients use CA-signed certificates to authenticate.
Learn more in Mutual TLS.
- Use Certificate-Bound Access Tokens
-
Indicate if access tokens issued to this client should be bound to the X.509 certificate that it uses to authenticate to the
access_tokenendpoint.If enabled, AM adds a confirmation key labelled
x5t#S256to all access tokens. The confirmation key contains the SHA-256 hash of the client’s certificate.Learn more in Certificate-bound proof-of-possession.
- Public key selector
-
Select the format of the public keys for JWT profile client authentication, ID token encryption, and mTLS self-signed certificate authentication. Valid formats are:
-
JWKs_URIConfigure a URI that exposes the client public keys in the Json Web Key URI field, and ensure the following related properties have sensible values for your environment:
-
JWKs URI content cache timeout in ms
-
JWKs URI content cache miss cache time
-
-
JWKsEnter a JWK Set containing one or more keys in the Json Web Key field. For example:
{ "keys": [ { "kty": "RSA", "n": "..." } ] } -
X509Enter a key object or a single certificate in one of the following fields, depending on the feature you are configuring:
-
(ID token encryption) Client ID Token Public Encryption Key. Requires an RSA public key object in X.509 PEM format. For example:
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- ...... -----END PUBLIC KEY-----For improved security and to support secret rotation, map the certificate to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.id.token.enc.public.keydynamic secret label instead, where identifier is the value of the Secret Label Identifier set in this client’s configuration. -
(JWT client authentication) Client JWT Bearer Public Key. Requires an X.509 certificate in PEM format. For example:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ..... -----END CERTIFICATE-----For improved security and to support secret rotation, map the certificate to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.jwt.public.keydynamic secret label instead, where identifier is the value of the Secret Label Identifier set in this client’s configuration. -
(mTLS client authentication) mTLS Self-Signed Certificate. Requires an X.509 certificate in PEM format. For example:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ..... -----END CERTIFICATE-----For improved security and to support secret rotation, map the certificate to the
am.applications.oauth2.client.identifier.mtls.trusted.certdynamic secret label, where identifier is the value of the Secret Label Identifier set in this client’s configuration.
-
Default:
JWKs_URI -
- User info response format.
-
The output format from the UserInfo endpoint.
Default: User info JSON response format.
The supported output formats are as follows:
-
User info JSON response format.
-
User info encrypted JWT response format.
-
User info signed JWT response format.
-
User info signed then encrypted response format.
Find more information on the output format of the UserInfo Response in the Successful UserInfo Response in the [ref]_OpenID Connect Core 1.0 incorporating errata set 1 _ specification.
-
- User info signed response algorithm
-
The JSON Web Signature (JWS) algorithm for signing UserInfo Responses. If specified, the response will be JSON Web Token (JWT) serialized, and signed using JWS.
The default, if omitted, is for the UserInfo Response to return the claims as a UTF-8-encoded JSON object using the
application/jsoncontent type. - User info encrypted response algorithm
-
The JSON Web Encryption (JWE) algorithm for encrypting UserInfo Responses.
If both signing and encryption are requested, the response will be signed then encrypted, with the result being a nested JWT.
The default, if omitted, is that no encryption is performed.
- User info encrypted response encryption algorithm
-
The JWE encryption method for encrypting UserInfo Responses. If specified, you must also specify an encryption algorithm in the User info encrypted response algorithm property.
AM supports the following encryption methods:
-
A128GCM,A192GCM, andA256GCM- AES in Galois Counter Mode (GCM) authenticated encryption mode. -
A128CBC-HS256,A192CBC-HS384, andA256CBC-HS512- AES encryption in CBC mode, with HMAC-SHA-2 for integrity.
Default:
A128CBC-HS256 -
- Request parameter signing algorithm
-
The JWS algorithm for signing the request parameter.
Must match one of the values configured in the Request parameter Signing Algorithms supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
- Request parameter encryption algorithm
-
The algorithm for encrypting the request parameter.
Must match one of the values configured in the Request parameter Encryption Algorithms supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
- Request parameter encryption method
-
The method for encrypting the request parameter.
Must match one of the values configured in the Request parameter Encryption Methods supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
Default:
A128CBC-HS256 - Token introspection response format
-
Specifies the format of the token introspection response. The possible values for this property are:
-
JSON response format
-
Signed JWT response format
-
Signed then encrypted JWT response format
Even if the client has configured the response to be JSON-formatted, it can request a signed JWT by adding the
"Accept: application/jwt"header to the request. However, when a client that’s configured to use either of the JWT-formatted responses requests a JSON response, AM returns an error. Find an example in /oauth2/introspect.The JWT response format follows the JWT Response for OAuth Token Introspection Internet Draft.
For related signing and encryption algorithms, refer to the following properties:
-
Token introspection response signing algorithm
-
Token introspection response encryption algorithm
-
Token introspection response encryption method
Default: JSON response format
-
- Token introspection response signing algorithm
-
Specifies the algorithm used to sign the token introspection response when it is formatted as a signed JWT.
Must match a value configured in the Token Introspection Response Signing Algorithms Supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
AM supports the following signing algorithms:
-
HS256- HMAC with SHA-256. -
HS384- HMAC with SHA-384. -
HS512- HMAC with SHA-512. -
ES256- ECDSA with SHA-256 and NIST standard P-256 elliptic curve. -
ES384- ECDSA with SHA-384 and NIST standard P-384 elliptic curve. -
ES512- ECDSA with SHA-512 and NIST standard P-521 elliptic curve. -
RS256- RSASSA-PKCS-v1_5 using SHA-256. -
RS384- RSASSA-PKCS-v1_5 using SHA-384. -
RS512- RSASSA-PKCS-v1_5 using SHA-512. -
EdDSA- EdDSA with SHA-512.The signing key used depends on the algorithm chosen. The following tables show the secret labels and their default signing key aliases:
This shows the secret label used to sign OpenID Connect ID tokens and backchannel logout tokens:
Secret label Default alias Algorithms(1) am.services.oauth2.oidc.signing.ES256es256testES256
am.services.oauth2.oidc.signing.ES384es384testES384
am.services.oauth2.oidc.signing.ES512es512testES512
am.services.oauth2.oidc.signing.RSArsajwtsigningkeyPS256
PS384
PS512
RS256
RS384
RS512am.services.oauth2.oidc.signing.EDDSAEdDSA with SHA-512
(1) The following applies to confidential clients only:
If you select an HMAC algorithm for signing ID tokens (HS256, HS384, or HS512), the Client Secret property value in the OAuth 2.0 Client is used as the HMAC secret instead of an entry from the secret stores.
Because AM and the client share the HMAC secret, a malicious user compromising the client could potentially create tokens that AM would trust. To protect against misuse, AM also signs the token using a non-shared signing key configured in the
am.services.oauth2.jwt.authenticity.signingsecret label.
Default: RS256
-
- Token introspection response encryption algorithm
-
The algorithm used to encrypt the token introspection response when it’s formatted as a signed then encrypted JWT.
Must match a value configured in the Token Introspection Response Encryption Algorithms Supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
AM supports the following encryption algorithms:
-
A128KW- AES Key Wrapping with 128-bit key derived from the client secret. -
A192KW- AES Key Wrapping with 192-bit key derived from the client secret. -
A256KW- AES Key Wrapping with 256-bit key derived from the client secret. -
RSA-OAEP- RSA with Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP) with SHA-1 and MGF-1. -
RSA-OAEP-256- RSA with OAEP with SHA-256 and MGF-1. -
RSA1_5- RSA with PKCS#1 v1.5 padding. -
dir- Direct encryption with AES using the hashed client secret. -
ECDH-ES- Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman -
ECDH-ES+A128KW- Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman + AES Key Wrapping with 128-bit key. -
ECDH-ES+A192KW- Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman + AES Key Wrapping with 192-bit key. -
ECDH-ES+A256KW- Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman + AES Key Wrapping with 256-bit key.
The algorithms that aren’t derived from the client secret use the client’s public keys. Learn more in the Public key selector property.
-
Default: RSA-OAEP-256
- Token introspection response encryption method
-
Specifies the encryption method used to encrypt the token introspection response when it’s formatted as a signed then encrypted JWT.
Must match a value configured in the Token Introspection Response Encryption Methods Supported property of the OAuth2 Provider service.
Refer to Advanced OpenID Connect.
AM supports the following encryption methods:
-
A128GCM,A192GCM, andA256GCM- AES in Galois Counter Mode (GCM) authenticated encryption mode. -
A128CBC-HS256,A192CBC-HS384, andA256CBC-HS512- AES encryption in CBC mode, with HMAC-SHA-2 for integrity.
Default: A128CBC-HS256
-
UMA
- Client Redirection URIs
-
This property is for future use, and not currently active. One or more allowable URIs to which the client can be redirected after the UMA claims collection process. The URIs mustn’t contain a fragment (
#).If multiple URIs are registered, the client MUST specify the redirection URI to be redirected to following approval.
OAuth2 Provider Overrides
- Enable OAuth2 Provider Overrides
-
Enable the OAuth 2.0 provider configuration to be overridden by the settings in this section.
When enabled, these client-level attributes override the corresponding attributes set by the OAuth 2.0 provider service or group.
The overriding attributes will only apply if this setting is enabled.
- Issue Refresh Tokens
-
Whether to issue a refresh token when returning an access token.
- Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens
-
Whether to issue a refresh token when refreshing an access token.
- Use Policy Engine for Scope decisions
-
With this setting enabled, the policy engine is consulted for each scope value that’s requested.
Scope decisions based on the policy engine are determined in the following way:
-
If a policy returns an action of GRANT=true, the scope is consented automatically, and the user isn’t consulted in a user-interaction flow.
-
If a policy returns an action of GRANT=false, the scope isn’t added to any resulting token, and AM doesn’t display it to the user in a user-interaction flow.
-
If no policy returns a value for the GRANT action:
-
For user-facing grant types, such as the authorization or device code flows, the user is asked for consent or saved consent is used.
-
For grant types that aren’t user-facing, such as those using password or client credentials, the scope isn’t added to any resulting token.
-
-
- Scopes Policy Set
-
The policy set that defines the context in which policy evaluations occur when
Use Policy Engine for Scope decisionsis enabled. Leave blank to use the defaultoauth2Scopespolicy set. - Access Token Modification Plugin Type
-
This setting determines the type of plugin that’s invoked:
-
SCRIPTEDto run the script defined inAccess Token Modification Script. -
JAVAto run the class defined inAccess Token Modifier Plugin Implementation Class. -
PROVIDERto use the access token modification plugin settings configured on the OAuth2 provider.
Default value:
PROVIDER -
- Access Token Modification Script
-
This script is run when issuing an access token. The script lets you modify the token, for example, by altering the data fields, before it is persisted or returned to the client.
The script is run if
Access Token Modification Plugin Typeis set toSCRIPTED.Learn more in Access token modification.
Default value:
--- Select a script --- - Access Token Modification Plugin Implementation Class
-
The Java class that provides the custom implementation for the access token modifier plugin interface,
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.AccessTokenModifier. This class is invoked whenAccess Token Modification Plugin Typeis set toJAVA.Default value:
[Empty] - OAuth2 Access Token May Act Script
-
The script that’s executed when issuing an access token explicitly to modify the
may_actclaim placed on the token.Refer to Token exchange.
Default value:
--- Select a script --- - OIDC ID Token May Act Script
-
The script that’s executed when issuing an OpenID Connect ID token explicitly to modify the
may_actclaim placed on the token.Default value:
--- Select a script --- - OIDC Claims Plugin Type
-
This setting can have the following possible values:
-
SCRIPTEDto run the script defined inOIDC Claims Script. -
JAVAto run the class defined inOIDC Claims Plugin Implementation Class. -
PROVIDERto use the OIDC claims plugin settings configured on the OAuth2 provider.
Default value:
PROVIDER -
- OIDC Claims Script
-
This script is run when issuing an ID token or during a request to the
/userinfoOIDC endpoint. Use this script to retrieve claim values based on an issued access token.The script is run if
OIDC Claims Plugin Typeis set toSCRIPTED.Default value:
--- Select a script --- - OIDC Claims Plugin Implementation Class
-
The Java class that provides the custom implementation for the OIDC claims plugin interface,
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.UserInfoClaimsPlugin. This class is invoked whenOIDC Claims Plugin Typeis set toJAVA.Default value:
[Empty] - Custom Login URL Template
-
Supports Freemarker syntax, with the following variables:
Variable
Description
gotoUrlThe URL to redirect to after login.
acrValuesThe Authentication Context Class Reference (acr) values for the authorization request.
realmThe AM realm the authorization request was made on.
moduleThe name of the AM authentication module requested to perform resource owner authentication.
serviceThe name of the AM authentication chain requested to perform resource owner authentication.
localeA space-separated list of locales, ordered by preference.
The following example template redirects users to a non-AM front end to handle login, which will then redirect back to the
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint with any required parameters:http://mylogin.com/login?goto=${goto}<#if acrValues??>&acr_values=${acrValues}</#if><#if realm??>&realm=${realm}</#if><#if module??>&module=${module}</#if><#if service??>&service=${service}</#if><#if locale??>&locale=${locale}</#if>The default AM login page is constructed using the base URL source service. - Use Client-Side Access & Refresh Tokens
-
When enabled, AM issues client-side access and refresh tokens that can be inspected by resource servers.
- Encrypt Client-Side Tokens
-
Whether client-side access and refresh tokens should be encrypted.
Enabling token encryption will disable token signing as encryption is performed using direct symmetric encryption.
- Allow Clients to Skip Consent
-
If enabled, clients can be configured so that the resource owner won’t be asked for consent during authorization flows.
- Enable Remote Consent
-
Enables consent to be gathered by a separate service.
- Remote Consent Service ID
-
The ID of an existing remote consent service agent.
- Scope Evaluation Plugin Type
-
This setting can have the following possible values:
-
SCRIPTEDto run the script defined inScope Evaluation Script. -
JAVAto run the class defined inScope Evaluation Plugin Implementation Class. -
PROVIDERto use the scope evaluation plugin settings configured on the OAuth2 provider.
Default value:
PROVIDER -
- Scope Evaluation Script
-
This script retrieves and evaluates the scope information for an OAuth2 access token.
The script lets you populate the scopes with profile attribute values. For example, if one of the scopes is
mail, AM setsmailto the resource owner’s email address in the token information returned.Default value:
--- Select a script --- - Scope Evaluation Plugin Implementation Class
-
The Java class that provides the custom implementation for the evaluate scope plugin interface: org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.ScopeEvaluator.
Default value:
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.registry.DefaultScopeEvaluator - Scope Validation Plugin Type
-
This setting can have the following possible values:
-
SCRIPTEDto run the script defined inScope Validation Script. -
JAVAto run the class defined inScope Validation Plugin Implementation Class. -
PROVIDERto use the scope validation plugin settings configured on the OAuth2 provider.
Default value:
PROVIDER -
- Scope Validation Script
-
This script validates and customizes the set of requested scopes for authorize, access token, refresh token, and back channel authorize requests.
Default value:
--- Select a script --- - Scope Validation Plugin Implementation Class
-
The Java class that provides the custom implementation for the evaluate scope plugin interface: org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.ScopeValidator.
Default value:
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.registry.DefaultScopeValidator - Authorize Endpoint Data Provider Plugin Type
-
This setting can have the following possible values:
-
SCRIPTEDto run the script defined inAuthorize Endpoint Data Provider Script. -
JAVAto run the class defined inAuthorize Endpoint Data Provider Plugin Implementation Class. -
PROVIDERto use the Authorize Endpoint Data Provider plugin settings configured on the OAuth2 provider.
Default value:
PROVIDER -
- Authorize Endpoint Data Provider Script
-
Use this script to retrieve additional data from an authorization request, such as data from the user’s session or from an external service.
Default value:
--- Select a script --- - Authorize Endpoint Data Provider Plugin Implementation Class
-
The Java class that provides the custom implementation for the evaluate scope plugin interface: org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.AuthorizeEndpointDataProvider.
Default value:
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.plugins.registry.DefaultEndpointDataProvider - Overrideable Id_Token Claims
-
List of claims in the ID token that can be overridden in the OIDC claims script. These should be the subset of the core OpenID Connect claims; for example
audorazp.
Some client configuration will depend on the configuration of the authorization server, and the type of client you are registering.
Configuration tips
Some basic points you must decide on are:
-
Is the client public or confidential?
-
What’s its redirection URI?
-
Which scopes does it need?
-
What’s the name this client will show as in the UI pages?
-
Which grant types the client can use to request tokens?
-
Which tokens can this client request?
-
In the case of an OpenID Connect client:
-
If the client is confidential, which authentication method will it use?
-
Which claims does the client need?
-
-
When finished, save your work.
| To create and manage a large number of clients without impacting system performance, use Scalable OAuth 2.0 clients. |
Shared application settings
To define shared settings for multiple client application profiles, you have these alternatives:
-
Configure default settings for all clients in the realm.
Client applications inherit their default settings from the OAuth 2.0 provider service. Find the settings in the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Services > OAuth2 Provider.
-
Create an OAuth 2.0 client profile group.
Client applications that belong to the group can inherit its settings.
Create group settings
-
In the AM admin UI, go to Realms > Realm Name > Applications > OAuth 2.0 > Clients.
-
On the Groups tab, click + Add Group, and click Create.
-
Adjust the configuration as needed, saving changes on each tab.
Inherit group settings
-
In the AM admin UI, go to Realms > Realm Name > Applications > OAuth 2.0 > Clients > Client ID.
-
On the Core tab, select the Group in the drop-down.
-
Save your work.
Selecting a group refreshes the client configuration, discarding any other unsaved settings.
Inheritance icons appear next to inherited group settings. Not all properties can inherit their value; for example, the Client secret property is specific to each client application.
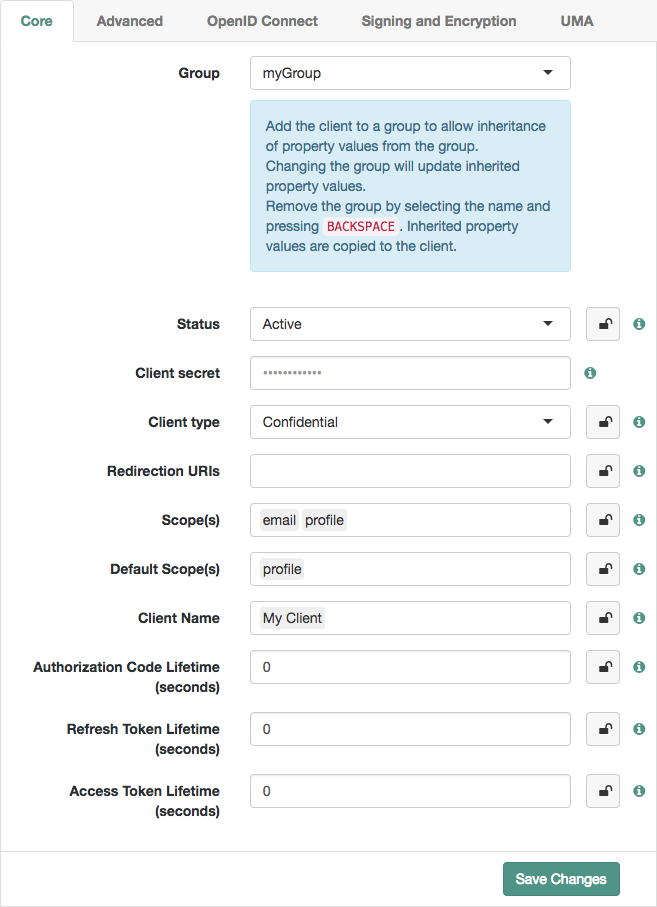 Figure 1. Inheriting group settings
Figure 1. Inheriting group settings -
Inherit settings by clicking their inheritance icons .
The icon changes to , indicating the setting is inherited.
-
Save your work.
Configuration changes have the following effects:
-
When you change inherited settings in the group, the client applications get them automatically.
-
When you change a client application’s Group, locked settings inherit from the new group.
-
When you remove or delete a group, AM writes inherited settings to the client profile, which you can edit independently.