Reference
This reference section covers service provider (SP), identity provider (IdP), and circle of trust (CoT) configuration properties. For the global services reference, see Reference.
Hosted IdP configuration
After you’ve set up a hosted IdP, you can configure it through the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Applications > Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Assertion content
The following groups appear under the Assertion Content tab:
Signing and Encryption
- Request/Response Signing
-
Specifies which parts of messages the IdP requires the SP to sign digitally.
- Encryption
-
When selected, the SP must encrypt NameID elements.
- Secret ID and Algorithms
-
- Secret ID Identifier
-
Specifies an identifier for the secret ID AM uses for this entity provider, when resolving secrets.
For example, when this value is set to
demo, the entity provider will use the following secret IDs:-
am.applications.federation.entity.providers.saml2.demo.signing -
am.applications.federation.entity.providers.saml2.demo.encryption
-
If not specified, AM uses the entity provider role-specific, default global secret IDs. For more information, see Secret ID mappings for SAML 2.0 signing and encryption.
- Signing Algorithm
-
The algorithms the provider can use to sign the request/response attributes selected in the Request/Response Signing group.
These algorithms are exposed in the provider’s metadata extension.
This property has no default.
- Digest Algorithm
-
The digest algorithms the provider can use when signing the requests and responses selected in the Request/Response Signing group.
These algorithms are exposed in the provider’s metadata extension.
This property has no default.
- Encryption Algorithm
-
This field specifies two types of encryption algorithms for the provider:
-
Symmetric algorithms, which the provider can use to encrypt the objects selected in the Encryption group. Select one or more AES algorithms from the drop-down list.
Default:
http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc -
Asymmetric algorithms, advertised as the provider’s transport key algorithm. When SAML 2.0 token encryption is enabled, hosted providers should use the algorithm the remote provider is advertising when encrypting symmetric encryption keys.
Select one or more algorithms from the drop-down list:
Key transport algorithms
-
http://www.w3.org/2009/xmlenc11#rsa-oaep.
When this algorithm is configured, AM will use the Mask Generation Function Algorithm property (Configure > Global Services > Common Federation Configuration) to create the transport key.
For a list of supported mask generation function algorithms, see Algorithms.
-
http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5.
For security reasons, you shouldn’t use this option.
-
NameID Format
- NameID Format List
-
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on.
The following diagram shows how the hosted IdP decides which of the supported NameID formats is used:
- NameID Value Map
-
Maps a NameID format (Key) to a user profile attribute (Value). The
persistentandtransientNameID formats don’t have to be mapped.The mapped user profile attribute must exist in your identity store. To find available attributes, go to Realms > Realm Name > Identity Stores > Identity Store Name > User Configuration and review the list under LDAP User Attributes. Find the default list of user profiles attributes for DS in LDAP User Attributes.
NameID mapping supports Base64-encoded binary values. Select the Binary option to Base64-encode the attribute’s value before it’s added to the assertion.
Authentication Context
- Mapper
-
A class that implements the
IDPAuthnContextMapperinterface and sets up the authentication context.Default value:
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultIDPAuthnContextMapper - Authentication Context
-
Maps the authentication context classes supported by the IdP and the authentication mechanisms used by AM when an SP specifies an authentication context class in a SAML 2.0 request.
- Context Reference
-
Select from the following options to define a context reference:
-
Predefined Reference to choose from a list of supported context references.
-
Custom Reference to type your own reference to an authentication context.
-
- Key
-
Select an authentication mechanism from the list for AM to use when the SP specifies an authentication context class in a SAML 2.0 request.
Authentication mechanisms
- Service
-
Specify an authentication tree for AM to use to authenticate the end user.
For example, in the Value field, enter
HmacOneTimePasswordto use the built-in one-time passcode (OTP) example authentication tree. - Module
-
AM will use the specified authentication module to authenticate the user.
- Authentication Level
-
AM will authenticate the user with a method that has an associated authentication level equal to or higher than the specified value.
If there is more than one suitable method, AM presents the available options by using a
ChoiceCallback.For more information on using and returning callbacks during authentication, see Authenticate over REST.
The RoleandUseroptions are deprecated. Don’t use these options. - Value
-
The name of the authentication mechanism you selected from the Key list. For example, if you chose
Serviceas the authentication mechanism, enter the name of an authentication tree. - Level
-
The order of precedence of the supported context reference classes as a numeric value.
Classes with higher numbers are considered stronger than lower numbered classes.
The values determine which authentication classes can be used
when the SP makes an authentication request that uses a comparison attribute;
for example, minimum or better.
The value of this field should match the auth level of the service. For example, if you configured an authentication mechanism as a tree that sets an auth level of 10, set the same value as you specified in the Level field. Because AM compares the current auth level against the level specified in Authentication Context table, if the two values don’t match, AM could require a logged-in user to re-authenticate.
Example
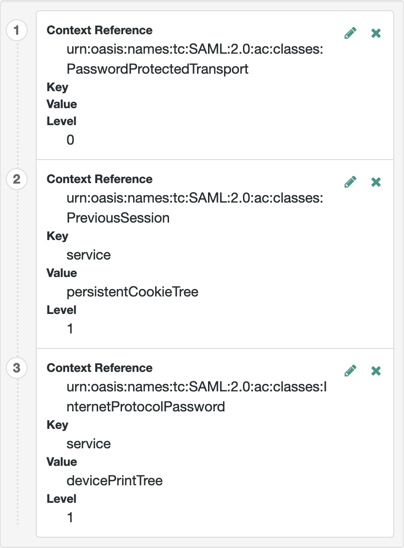
+ For more information on authentication context classes, see Authentication Context for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0 in the SAML 2.0 Standard.
+
Default value: urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport
Assertion processing
The following properties appear under the Assertion Processing tab:
Attribute Mapper
Learn more in IDP attribute mapper.
- Attribute Mapper
-
The Java class for a custom Attribute Mapper. This class isn’t invoked if a script is selected for
Attribute Mapper Script.Default:
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultIDPAttributeMapper - Attribute Mapper Script
-
The script for a custom Attribute Mapper.
Select from a list of all the
Saml2 IDP Attribute Mappertype scripts saved to this realm, including the default template script,SAML2 IDP Attribute Mapper Script.For details, see saml2-idp-attribute-mapper.js.
- Attribute Map
-
Map SAML attributes to user profile attributes.
Before user profile attributes can be mapped, they must be allowed in user profiles and also specified for the identity repository. Find more information in Add custom user profile attributes.
To see the profile attributes available for an LDAP identity repository, log in to the AM admin UI, and go to Realms > Realm Name > Identity Stores > User Configuration. Check the LDAP User Attributes list.
By default, you can map single-valued attributes to either user profile attributes or static values.
To map a static value, enclose the value in double quotes ("), for example:
 Figure 1. Example of mapping a static value
Figure 1. Example of mapping a static valueTo map multi-valued attributes, you must implement a custom IdP attribute mapper.
Account Mapper
- Account Mapper
-
The class that implements an
AccountMapperto map remote users to local user profiles. - Disable NameID Persistence
-
Disables the storage of the NameID values in the user data store for all NameIDs issued by the IdP instance as long as the NameID format is anything but the persistent NameID format:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent. That is, you can disable the storage of NameID values with persistent NameID-Format if and only if there is a NameID value mapping set up for the NameID-Format.By preventing the storage of the NameID values, the
ManageNameIDand theNameIDMappingSAML profiles won’t work when using any persistent NameID formats. Existing account links that have been established and stored aren’t removed when disabling NameID persistence.Default value:
false
Local Configuration
- Auth URL
-
An alternative URL for authenticating users, for example, if you have created a custom user interface other than the UI.
If present, this overrides the default UI login URL used to authenticate users during federation.
The specified authentication URL is responsible for authenticating the federated user and must establish a session in AM, and return the SSO token value in the configured cookie name, usually
iPlanetDirectoryPro.The domain of the authentication URL must be configured in AM so that the cookie is accepted, and if host cookies are configured in AM, then the fully qualified domain name of the authentication URL must be identical to that of the AM instance.
For more information on configuring the domains AM accepts in the SSO cookies, see Change the cookie domain.
AM redirects users to the URL specified, and appends a
gotoparameter. The parameter contains the URL the user must be redirected to after authentication. The specified authentication URL mustn’t override thegotoparameter, as that would redirect the user elsewhere and federation will fail.For more information, see Success and failure redirection URLs.
- Reverse Proxy URL
-
The reverse proxy URL if a reverse proxy is used for SAML endpoints.
- External Application Logout URL
-
The URL to which to send an HTTP POST including all cookies when receiving a logout request. To add a user session property as a POST parameter, include it in the URL query string as a
appsessionpropertyparameter.
Services
The following properties appear under the Services tab:
- MetaAlias
-
The MetaAlias value used to locate the provider’s entity identifier, specified as
[/realm-name]*/provider-name, where provider-name can’t contain slash characters (/). For example:/myRealm/mySubrealm/idp.Ensure the MetaAlias is unique for each provider configured in a CoT and in the realm.
IDP Service Attributes
- Artifact Resolution Service
-
The endpoint to manage artifact resolution. The Index is a unique number identifier for the endpoint.
- Single Logout Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Single SignOn Service
-
The endpoints to manage single sign-on.
These endpoints are used only for SP-initiated flows but are included as a requirement of the SAML V 2.0 Metadata specification.
- Assertion ID Request Service
-
The endpoints to request for a specific assertion by referring to its assertion ID.
Advanced settings
The following properties appear under the Advanced tab:
SAE Configuration
- IDP URL
-
The endpoint to manage Secure Attribute Exchange requests.
- Application Security Configuration
-
Indicate how encryption for Secure Attribute Exchange operations should be handled.
ECP Configuration
- IDP Session Mapper
-
The class that finds a valid session from an HTTP servlet request to an IdP with a SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy profile.
Session Synchronization
- Enabled
-
Select this option to make the IdP send a SOAP logout request over the back channel to all SPs when a session times out. A session can time out when the maximum idle time or maximum session time is reached, for example.
IDP Finder Implementation
- IDP Finder Implementation Class
-
The class that finds the preferred IdP to handle a proxied authentication request.
- IDP Finder JSP
-
The JSP that presents the list of IdPs to the user.
- Enable Proxy IDP Finder For All SPs
-
Select this option to apply the finder for all remote SPs.
Relay State URL List
- Relay State URL List
-
A list of URLs permitted for the
RelayStateparameter. For SLO operations, AM validates the redirection URL in theRelayStateparameter against this list. If theRelayStateparameter’s value is in the list, AM allows redirection to theRelayStateURL. If it isn’t in the list, a browser error occurs.Use the pattern matching rules described in Success and failure redirection URLs to specify URLs in the list.
If you don’t specify any URLs in this property, AM only allows redirection to
RelayStateURLs that match the domain of the instance. Any other URL causes a browser error.This property doesn’t apply to IdP-initiated SSO, where the validation of the
RelayStateparameter should be performed on the SP.
IDP Adapter
Learn more in IDP adapter.
- IDP Adapter Class
-
The Java class for a custom IdP Adapter.
This class isn’t invoked if a script is selected for
IDP Adapter Script. - IDP Adapter Script
-
The script for a custom IdP Adapter.
Select from a list of all the
Saml2 IDP Adaptertype scripts saved to this realm, including the default template script,SAML2 IDP Adapter Script.For details, see saml2-idp-adapter.js.
Remote IdP configuration
After you’ve set up a remote IdP, configure it through the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Applications > Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Assertion content
The following properties appear under the Assertion Content tab:
- Request/Response Signing
-
Specifies which parts of messages the identity provider requires the service provider to sign digitally.
- Encryption
-
When selected, the service provider must encrypt NameID elements.
- NameID Format List
-
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on.
- Enabled, User Name, Password
-
When enabled, authenticate with the specified user name and password at SOAP endpoints.
Services
The following properties appear under the Services tab:
- Artifact Resolution Service
-
Specifies the endpoint to manage artifact resolution. The Index is a unique identifier for the endpoint.
- Single Logout Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Single SignOn Service
-
The endpoints to manage single sign-on.
These endpoints are used only for SP-initiated flows but are included as a requirement of the SAML V 2.0 Metadata specification.
- URL
-
Specifies the endpoint to manage name identifier mapping.
Hosted SP configuration
After you’ve set up a hosted SP, you can configure it through the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Applications > Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Assertion content
The following properties appear under the Assertion Content tab:
- Request/Response Signing
-
The parts of messages the SP requires the IdP to sign digitally.
- Encryption
-
The IdP must encrypt selected elements.
- Secret ID and Algorithms
-
- Secret ID Identifier
-
Specifies an identifier for the secret ID AM uses for this entity provider, when resolving secrets.
For example, if you set this value to
demo, the entity provider uses the following secret labels:-
am.applications.federation.entity.providers.saml2.demo.signing -
am.applications.federation.entity.providers.saml2.demo.encryption
If not specified, AM uses the entity provider role-specific, default global secret labels. Learn more in Secret label mappings for SAML 2.0 signing and encryption.
-
- Signing Algorithm
-
The algorithms the provider can use to sign the request/response attributes selected in the Request/Response Signing group.
These algorithms are exposed in the provider’s metadata extension.
This property has no default.
- Digest Algorithm
-
The digest algorithms the provider can use when signing the requests and responses selected in the Request/Response Signing group.
These algorithms are exposed in the provider’s metadata extension.
This property has no default.
- Encryption Algorithm
-
This field specifies two types of encryption algorithms for the provider:
-
Symmetric algorithms, which the provider can use to encrypt the objects selected in the Encryption group. Select one or more AES algorithms from the drop-down list.
Default:
http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc -
Asymmetric algorithms, advertised as the provider’s transport key algorithm. When SAML 2.0 token encryption is enabled, hosted providers should use the algorithm the remote provider is advertising when encrypting symmetric encryption keys.
Select one or more algorithms from the drop-down list:
Key transport algorithms
-
http://www.w3.org/2009/xmlenc11#rsa-oaep.
When this algorithm is configured, AM will use the Mask Generation Function Algorithm property (Configure > Global Services > Common Federation Configuration) to create the transport key.
For a list of supported mask generation function algorithms, see Algorithms.
-
http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5.
For security reasons, we strongly recommend that you do not use this option.
-
- NameID Format List
-
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on.
The following diagram shows how the hosted SP decides which of the supported NameID formats is used:
- Disable NameID Persistence
-
Disables the storage of NameIDs in the user data store, even if the
NameIDformat isurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentin the received assertion and the account mapper has identified the local user.You may want to disable storage of NameID values if you are using a read-only data store, or an external identity store that does not have the AM identity schemas applied.
When local authentication is utilized for account linking purposes, disabling federation persistence requires end users to authenticate locally for each SAML-based login.
Default value:
false
Authentication Context
- Mapper
-
A class that implements the
SPAuthnContextMapperinterface and maps the incoming request parameters to an authentication context.Default:
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultSPAuthnContextMapper - Authentication Context
-
The authentication context maps the URI references to IdP’s supported authentication context classes to authentication levels set on the SP side.
- Context Reference
-
Select from the following options to define a context reference:
-
Predefined Reference to choose from a list of supported context references.
-
Custom Reference to type your own reference to an authentication context.
-
- Level
-
The order of precedence of the supported context reference classes as a numeric value.
Classes with higher numbers are considered stronger than lower numbered classes. The values determine which authentication classes can be used when the SP makes an authentication request that uses a comparison attribute; for example,
minimumorbetter.Example
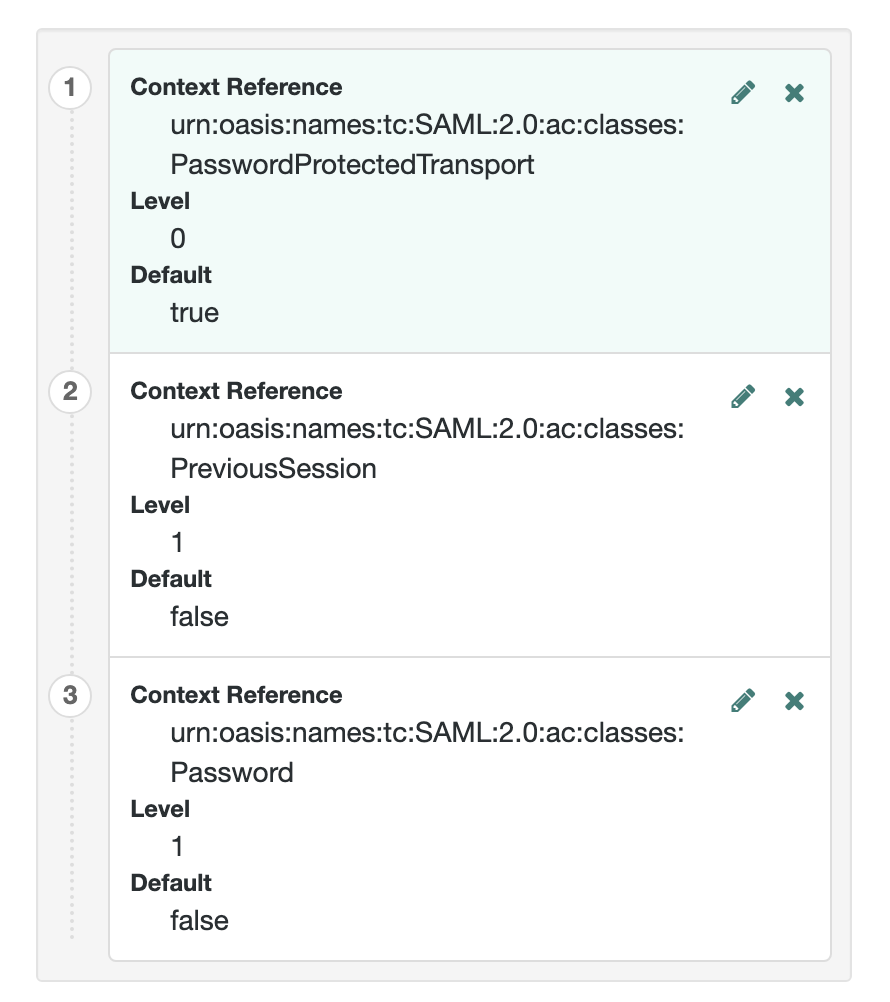
For more information on authentication context classes, see Authentication Context for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0 in the SAML 2.0 Standard.
Default value:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport
- Comparison Type
-
Used in conjunction with the default authentication context to specify the possible range of authentication mechanisms the IdP can choose from.
For example, if the Comparison Type field is set to
better, and thePasswordProtectedTransportauthentication context class is selected in the Default Authentication Context field, the IdP must select an authentication mechanism with a higher level assigned.Default:
exact - Include Request Authentication Context
-
Specifies whether to include an authentication context class as the Requested Authentication Context in the SAML 2.0 Authentication Request.
Default: Enabled
- Assertion Time Skew
-
Grace period in seconds for the
NotBeforetime in assertions.
- Enabled, User Name, Password
-
When enabled, authenticate with the specified user name and password at SOAP endpoints.
Assertion processing
The following properties appear under the Assertion Processing tab:
- Attribute Mapper
-
Specifies a class that implements the attribute mapping.
- Attribute Map
-
Maps SAML attributes to session properties, or user profile attributes.
The value of Key is a SAML attribute sent in an assertion, and the value of Value is a property in the user’s session, or an attribute of the user’s profile.
By default, the SP maps the SAML attributes it receives to equivalent-named session properties. However, when the SP is configured to create identities during autofederation and the identity does not exist yet, the SP maps the SAML attributes to their equivalents in the newly-created user profile.
The special mapping
Key: *, Value: *means that the SP maps each attribute it receives in the assertion to equivalent-named properties or attributes. For example, if the SP receivesmailandfirstnamein the assertion, it maps them tomailandfirstnamerespectively.Remove the special mapping and add key pairs to the map if:
-
(During autofederation) The attributes in the IdP’s and the SP’s identity stores do not match.
-
You need control over the names of the session properties.
-
You need control over which attributes the SP should map, because the IdP adds too many to the assertion.
For example, if the the SAML attribute is
firstnameand you want the SP to map it to a session property/user profile attribute calledcn, create a mapping similar toKey: firstname, Value: cn. -
- Enabled
-
When enabled, automatically federate user’s accounts at different providers based on the specified SAML attribute.
- Attribute
-
Specifies the SAML attribute to match accounts at different providers.
- Account Mapper
-
Specifies a class that implements
AccountMapperto map remote users to local user profiles. - Use Name ID as User ID
-
When selected, fall back to using the name identifier from the assertion to find the user.
- Transient User
-
The user profile to map all IdP users when sending transient name identifiers.
- Artifact Message Encoding
-
Specifies the message encoding format for artifacts.
- Local Authentication URL
-
Use this property to specify an alternative URL to redirect the user to after validating the SAML2 assertion from the IDP. For example, if you have created a custom user interface other than the AM UI.
When in integrated mode, the query parameters are appended to the configured URL. Typically, these parameters contain all the information necessary for AM to continue the authentication journey.
When in standalone mode, AM redirects users to the specified URL, and appends a
gotoparameter. This parameter contains the URL the user must be redirected to next. - Intermediate URL
-
Specifies a URL to which the user is redirected after authentication but before the original URL requested.
- External Application Logout URL
-
Specifies the URL to which to send an HTTP POST including all cookies when receiving a logout request. To add a user session property as a POST parameter, include it in the URL query string as a
appsessionpropertyparameter.
- Default Relay State URL
-
Specifies the URL to which to redirect users after the request has been handled. Used if not specified in the response.
- Adapter
-
Specifies a class that implements the
FederationSPAdapterinterface and performs application specific processing during the federation process. - Adapter Environment
-
Specifies environment variables passed to the adapter class.
Services
The following properties appear under the Services tab:
- MetaAlias
-
Used to locate the hosted provider’s entity identifier, specified as
[/realm-name]*/provider-name, where provider-name can not contain slash characters (/). For example:/myRealm/mySubrealm/sp.Ensure the MetaAlias is unique for each provider configured in a CoT and in the realm.
- Single Logout Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Assertion Consumer Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to consume assertions, with Index corresponding to the index of the URL in the standard metadata.
The scheme, FQDN, and port configured must exactly match those of the SP as they appear in its metadata.
To determine the SP’s endpoint URL, AM uses the Base URL service, if configured.
If the URL does not match, the SAML 2.0 flow will fail and AM will log
Invalid Assertion Consumer Location specifiedin the audit log file.
Advanced settings
The following properties appear under the Advanced tab:
- SP URL
-
Specifies the endpoint to manage Secure Attribute Exchange requests.
- SP Logout URL
-
The endpoint of the SP that can handle global logout requests.
- Application Security Configuration
-
Specifies how to handle encryption for Secure Attribute Exchange operations.
- Request IDP List Finder Implementation
-
A class that returns a list of preferred IdPs trusted by the SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy profile.
- Request IDP List Get Complete
-
A URI reference used to retrieve the complete IdP list if the
IDPListelement is not complete. - Request IDP List
-
A list of IdPs for the SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy to contact, used by the default implementation of the IDP Finder.
- IDP Proxy
-
When enabled, AM includes a
Scopingelement in the authentication request to enable the request to be proxied. - Introduction
-
When enabled, use introductions to find the proxy IdP.
- Proxy Count
-
The maximum number of proxy IdPs.
- IDP Proxy List
-
A list of URIs identifying preferred proxy IdPs.
- Enabled
-
When enabled, the SP sends a SOAP logout request over the back channel to all IdPs when a session times out. A session may time out when the maximum idle time or maximum session time is reached, for example.
- Relay State URL List
-
List of URLs permitted for the
RelayStateparameter. AM validates the redirection URL in theRelayStateparameter against this list. If theRelayStateparameter’s value is in the list, AM allows redirection to theRelayStateURL. If it is not in the list, a browser error occurs.Use the pattern matching rules described in Success and failure redirection URLs to specify URLs in the list.
If you DO NOT specify any URLs in this property, AM only allows redirection to
RelayStateURLs that match the domain of the instance. Any other URL will cause a browser error.
Remote SP configuration
After you’ve set up a remote SP, configure it through the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Applications > Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Assertion content
The following properties appear under the Assertion Content tab:
- Request/Response Signing
-
Specifies what parts of messages the service provider requires the identity provider to sign digitally.
- Encryption
-
The identity provider must encrypt selected elements.
- NameID Format List
-
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on.
- Disable NameID Persistence
-
Disables the storage of NameID values at the IdP when generating an assertion for this remote SP.
Default value:
false
- Enabled, User Name, Password
-
When enabled, require authentication with the specified user name and password at SOAP endpoints.
Assertion processing
The following properties appear under the Assertion Processing tab:
- Attribute Map
-
Override any mappings of attributes to user profile attributes at the IdP.
- Encoding
-
Specifies the message encoding format for artifacts.
Services
The following properties appear under the Services tab:
- Single Logout Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to manage name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Assertion Consumer Service
-
Specifies the endpoints to consume assertions, with Index corresponding to the index of the URL in the standard metadata.
Advanced settings
The following properties appear under the Advanced tab:
- Skip Endpoint Validation For Signed Requests
-
When enabled, AM does not verify Assertion Consumer Service URL values provided in SAML authentication requests. This allows the Assertion Consumer Service URL to contain dynamic query parameters, for example.
As assertion consumer service URL verification is part of the SAML 2.0 spec, you can only skip validation if the authentication request is digitally signed by the SP. To digitally sign authentication requests, in the remote SP configuration go to Assertion Content > Signing and Encryption > Request/Response Signing, and select Authentication Requests Signed.
You must configure the remote SP to sign the authentication request.
AM returns an error if it receives an unsigned authentication request and this option is enabled.
- SP URL
-
Specifies the endpoint to manage Secure Attribute Exchange requests.
- SP Logout URL
-
The endpoint of the SP that can handle global logout requests.
- IDP Proxy enabled
-
When enabled, the authentication requests from this SP can be proxied.
- Proxy all requests
-
When enabled, AM proxies every authentication request from the SP, whether it contains a
Scopingelement or not.The IDP Proxy option must be enabled for this option to take effect.
- Introduction enabled
-
When enabled, use introduction cookies to find the proxy IdP.
This property only works with a non-default SAML2IDPProxyFRImpl implementation, and will be deprecated in a future release.
- Use IDP Finder
-
When enabled, use the IdP finder service to determine the IDP to which to proxy authentication requests.
- Proxy Count
-
Specifies the maximum number of proxy IdPs. AM sets the specified value in the
Scopingelement of the authentication request it proxies for this SP.You must enable Proxy all requests for this option to take effect.
- IDP Proxy List
-
A list of URIs identifying preferred proxy IdPs.
CoT configuration
Once you have set up a CoT, you can configure it through the AM admin UI under Realms > Realm Name > Applications > Federation > Circle of Trust > Circle of Trust Name.
- Name
-
String that refers to the circle of trust.
Once you have set up a circle of trust, the name cannot be configured.
- Description
-
Short description of the circle of trust.
- Status
-
Whether this circle of trust is operational.
- Entity Providers
-
Known hosted and remote identity and service providers participating in this circle of trust.
- SAML2 Writer Service URL
-
SAML 2.0 service that writes identity provider entity identifiers to Common Domain cookies after successful authentication, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
https://discovery.example.com:8443/openam/saml2writer. - SAML2 Reader Service URL
-
SAML 2.0 service that reads identity provider entity identifiers from Common Domain cookies, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
https://discovery.example.com:8443/openam/saml2reader.
SAML 2.0 advanced properties
To configure SAML 2.0 advanced properties, in the AM admin UI, go to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced.
openam.saml.decryption.debug.mode-
When enabled, AM decrypts SAML 2.0 messages that are sent and received, and writes the content to the debug logs.
As these messages may contain user information, you should not enable this property in production environments.
Default:
False org.forgerock.openam.saml2.authenticatorlookup.skewAllowance-
Specifies the allowable time difference, in seconds, between any existing session the user may have, and the current time when an authentication request specifies
ForceAuthn.If the authenticated user’s session was created outside of the allowable time range, AM rejects the assertion, and re-authentication is required.
Default:
60